https://epaper.lokmat.com/articlepage.php?articleid=LOKTIME_NSKF_20250416_3_5
S863: 10 Commands for Better Sciences, Society & Spirituality..
Ten Commandments for Sciences (Material, Social & Spiritual) and Rationalism.
Inspired by the lives and works of rationalists and thinkers such as Socrates, Bertrand Russell, Aryabhata, Thiruvalluvar, Basavanna, John Dewey, B.R. Ambedkar, and others, these commandments guide the pursuit of truth across material, social, and spiritual sciences through reason and rationalism:
- Interrogate All Claims with Rigor
Emulate Socrates’ relentless questioning to scrutinize material, social, and spiritual assertions, seeking truth through reason rather than assumption. - Ground Knowledge in Empirical Evidence
Like Aryabhata’s astronomical observations, anchor material science in data, social science in observable patterns, and spiritual inquiry in reflective experience. - Embrace Uncertainty with Openness
As Bertrand Russell advocated, accept the limits of knowledge in all sciences, remaining humble and adaptable to new evidence or perspectives. - Reason Logically Across Domains
Follow Thiruvalluvar’s clarity of thought, applying precise logic to material experiments, social theories, and spiritual philosophies alike. - Prioritize Ethical Impact
Inspired by Basavanna’s moral vision, ensure scientific pursuits—whether material, social, or spiritual—promote justice, compassion, and human dignity. - Test Ideas Through Practical Application
Adopt John Dewey’s pragmatism: validate material innovations, social policies, and spiritual practices by their real-world outcomes and benefits. - Foster Inclusive Inquiry
Reflecting Ambedkar’s fight for equality, democratize access to scientific and rational discourse, ensuring diverse voices shape material, social, and spiritual knowledge. - Synthesize Interdisciplinary Insights
Integrate material, social, and spiritual sciences, as ancient thinkers did, to create holistic understanding and avoid fragmented or dogmatic conclusions. - Speak Truth Boldly Yet Compassionately
Channel Socrates’ courage to challenge falsehoods in all realms, communicating findings with clarity and empathy to advance collective wisdom. - Pursue Liberation Through Knowledge
Use material science to solve practical problems, social science to dismantle oppression, and spiritual science to free minds, as Ambedkar and Russell envisioned, for a just and enlightened world.
S862: 10 Commandments for Science & Rationalism.
View, Verify & Validate the 10 Commandments of Sciencers.
Derive 10 Commandments for Science & Rationalism derived from life and works of Rationalists and great thinkers like Socrates, Russel, Aryabhatta, thiruvalluvar, Basavana, Dewey, Ambedkar..etc
By Grok
- Question Relentlessly
- Seek Evidence Above Authority
- Cultivate Humility in Knowledge
- Reason with Clarity and Precision
- Uphold Ethical Inquiry
- Embrace Experimentation and Pragmatism
- Champion Equality in Thought
- Integrate Diverse Perspectives
- Communicate Truth with Courage
- Pursue Knowledge for Liberation
Ten Commandments for Science & Rationalism
Drawing from the lives and works of great rationalists and thinkers such as Socrates, Bertrand Russell, Aryabhata, Thiruvalluvar, Basavanna, John Dewey, B.R. Ambedkar, and others, the following commandments encapsulate principles for pursuing truth, reason, and scientific inquiry:
- Question Relentlessly
Embrace Socratic inquiry by questioning assumptions, beliefs, and dogmas. Truth emerges through persistent, open-ended examination, not blind acceptance. - Seek Evidence Above Authority
As Aryabhata challenged prevailing astronomical models with observations, prioritize empirical evidence and reasoned arguments over tradition or authority. - Cultivate Humility in Knowledge
Acknowledge, like Bertrand Russell, that certainty is elusive. Admit ignorance where evidence is lacking and remain open to revising beliefs. - Reason with Clarity and Precision
Follow Thiruvalluvar’s emphasis on clear thought and expression. Articulate ideas logically, avoiding ambiguity and emotional bias in discourse. - Uphold Ethical Inquiry
Inspired by Basavanna’s moral integrity, ensure scientific and rational pursuits serve humanity’s well-being, rejecting exploitation or harm in the name of knowledge. - Embrace Experimentation and Pragmatism
Adopt John Dewey’s pragmatic approach: test ideas through action and experience, refining theories based on practical outcomes. - Champion Equality in Thought
Reflecting B.R. Ambedkar’s fight against dogma and inequality, promote inclusive rationalism, ensuring all voices have access to inquiry and debate. - Integrate Diverse Perspectives
Like the syncretic wisdom of ancient thinkers, synthesize knowledge across disciplines and cultures to enrich understanding and avoid narrow dogmatism. - Communicate Truth with Courage
Emulate Socrates’ fearless pursuit of truth, even in the face of opposition. Speak honestly, but with compassion, to advance collective understanding. - Pursue Knowledge for Liberation
As Ambedkar and Russell advocated, use science and reason to liberate minds from superstition, oppression, and ignorance, fostering a just and enlightened society.
These commandments reflect the shared ethos of rationalists and thinkers who valued reason, evidence, and humanity’s potential for growth through knowledge.
BY Meta A.I
Here are ten commandments for Science and Rationalism inspired by the lives and works of great thinkers:
Doubt Everything, Especially Thyself: Question assumptions, challenge prevailing wisdom, and seek evidence before accepting truths. (Inspired by Socrates)
Seek Knowledge Without Borders: Pursue knowledge fearlessly, unshackled by dogma, tradition, or authority. (Inspired by Aryabhatta and other pioneers of science)
Reason Over Emotion: Let logic and evidence guide decision-making, but acknowledge the role of emotions in human experience. (Inspired by Bertrand Russell)
Respect Dissent and Debate: Encourage critical thinking, foster open discussion, and value diverse perspectives. (Inspired by thinkers like Dewey and Ambedkar)
Empiricism Over Dogma: Ground beliefs and theories in empirical evidence and observation, rather than doctrine or hearsay. (Inspired by scientific method)
Cultivate Intellectual Humility: Recognize the limits of knowledge, acknowledge uncertainty, and revise beliefs based on new evidence. (Inspired by Socrates and Russell)
Promote Education and Critical Thinking: Empower individuals with knowledge, critical thinking skills, and intellectual curiosity. (Inspired by Thiruvalluvar and Basavanna)
Challenge Social Injustice with Reason: Use rational inquiry to identify and address social inequalities, promoting fairness and justice. (Inspired by Ambedkar and other social reformers)
Seek Interconnectedness and Holism: Understand phenomena in context, recognizing relationships between parts and wholes. (Inspired by various philosophical traditions)
Pursue Wisdom for the Greater Good: Apply knowledge and reason to improve human well-being, foster compassion, and promote the common good. (Inspired by the collective wisdom of rationalist thinkers)
These commandments aim to distill the essence of rationalist thought, encouraging a culture of critical thinking, intellectual curiosity, and pursuit of knowledge for the betterment of society.
Meta AI response: Here are ten commandments for Science and Rationalism inspired by the lives and works of great thinkers: Doubt Everything, Especially Thyself: Question assumptions, challenge prevailing wisdom, and seek evidence before accepting truths. (Inspired by Socrates) Seek Knowledge Without Borders: Pursue knowledge fearlessly, unshackled by dogma, tradition, or authority. (Inspired by Aryabhatta and other pioneers of science) Reason Over Emotion: Let logic and evidence guide decision-making, but acknowledge the role of emotions in human experience. (Inspired by Bertrand Russell) Respect Dissent and Debate: Encourage critical thinking, foster open discussion, and value diverse perspectives. (Inspired by thinkers like Dewey and Ambedkar) Empiricism Over Dogma: Ground beliefs and theories in empirical evidence and observation, rather than doctrine or hearsay. (Inspired by scientific method) Cultivate Intellectual Humility: Recognize the limits of knowledge, acknowledge uncertainty, and revise beliefs based on new evidence. (Inspired by Socrates and Russell) Promote Education and Critical Thinking: Empower individuals with knowledge, critical thinking skills, and intellectual curiosity. (Inspired by Thiruvalluvar and Basavanna) Challenge Social Injustice with Reason: Use rational inquiry to identify and address social inequalities, promoting fairness and justice. (Inspired by Ambedkar and other social reformers) Seek Interconnectedness and Holism: Understand phenomena in context, recognizing relationships between parts and wholes. (Inspired by various philosophical traditions) Pursue Wisdom for the Greater Good: Apply knowledge and reason to improve human well-being, foster compassion, and promote the common good. (Inspired by the collective wisdom of rationalist thinkers) These commandments aim to distill the essence of rationalist thought, encouraging a culture of critical thinking, intellectual curiosity, and pursuit of knowledge for the betterment of society.
S861: Ten Commandments for Students life.
Student’s Ten Commandments for Students’ Welfare and Future Success in Life, designed for Indian students, integrating scientific principles and moral values to foster personal growth, academic excellence, and ethical behavior.
Ten Commandments for Students’ Welfare and Future Success in Life
- Thou Shalt Pursue Knowledge with Curiosity
- Thou Shalt Practice Ethical Integrity
- Thou Shalt Respect Diversity and Inclusion
- Thou Shalt Manage Emotions Rationally
- Thou Shalt Prioritize Physical and Mental Health
- Thou Shalt Reject Violence and Harassment
- Thou Shalt Cultivate Discipline and Time Management
- Thou Shalt Engage in Community and Service
- Thou Shalt Embrace Failure as Growth
- Thou Shalt Plan for a Purposeful Future
This framework draws on the context of the Teachers-Students Safety Protocol 2025, addressing concerns like emotional volatility, communal tensions (e.g., the Samserganj incident), and the need to prevent sexual harassment or quid pro quo dynamics. It also incorporates the user’s prior interest in rationalism, ethics, and Indian philosophy (e.g., Nyaya, Ambedkar’s pragmatism) from conversation history, ensuring a balance of evidence-based reasoning and moral guidance. The commandments are grounded in psychological research, educational policies like NEP 2020, and Indian ethical traditions, with references to science and morality.
Ten Commandments for Students’ Welfare and Future Success in Life
1. Thou Shalt Pursue Knowledge with Curiosity
Embrace learning as a lifelong journey, driven by curiosity and critical thinking. Science shows that a growth mindset—believing abilities can improve through effort—enhances academic success (Dweck, 2006). Engage with subjects like math or history with the same rigor as Nyaya philosophers applied to logic, questioning assumptions and seeking evidence.
2. Thou Shalt Practice Ethical Integrity
Act with honesty and fairness in academics and relationships, avoiding cheating or exploitation. Moral philosophy, like Ambedkar’s emphasis on equality, underscores integrity as a foundation for trust. Resist quid pro quo temptations (e.g., exchanging favors for grades), which science links to eroded self-esteem and social harm (Baumeister, 1998).
3. Thou Shalt Respect Diversity and Inclusion
Treat peers and teachers with respect, regardless of religion, caste, or gender, fostering harmony in diverse settings like Indian classrooms. Psychological studies show inclusive environments reduce prejudice and boost collaboration (Allport, 1954). Learn from the Samserganj incident to counter communal tensions with empathy, not aggression.
4. Thou Shalt Manage Emotions Rationally
Temper emotional reactions with reason to avoid conflicts, as emotional volatility can “blind rationality” (per the query’s context). Neuroscience research highlights that mindfulness practices reduce amygdala-driven impulsivity (Davidson, 2003). Practice techniques like journaling or meditation, rooted in Buddhist traditions, to stay calm under stress.
5. Thou Shalt Prioritize Physical and Mental Health
Maintain well-being through exercise, sleep, and stress management, as science links health to cognitive performance (Ratey, 2008). Indian traditions, like yoga, promote balance, while NEP 2020 emphasizes holistic education. Seek counseling if needed, especially in high-pressure academic environments, to build resilience.
6. Thou Shalt Reject Violence and Harassment
Commit to non-violence and respect boundaries, avoiding physical or verbal aggression, including sexual harassment. Social psychology research shows zero-tolerance policies deter harmful behaviors (Berkowitz, 2003). Report inappropriate conduct, like quid pro quo advances, to ensure safe learning spaces, as outlined in the Safety Protocol.
7. Thou Shalt Cultivate Discipline and Time Management
Develop habits of punctuality and organization, as studies link self-discipline to higher achievement (Duckworth, 2007). Use tools like schedules or apps, inspired by the structured learning of ancient Indian Gurukuls, to balance studies, hobbies, and rest for long-term success.
8. Thou Shalt Engage in Community and Service
Contribute to society through volunteering or peer support, reflecting the Indian value of seva (selfless service). Social science research shows altruism enhances life satisfaction and social bonds (Harbaugh, 2007). Join initiatives like the All-India Teachers Unity Group’s student counterparts to build leadership.
9. Thou Shalt Embrace Failure as Growth
View setbacks as opportunities to learn, not as defeats. Cognitive science supports that resilience—adapting to failure—predicts future success (Seligman, 2011). Draw inspiration from rationalist thinkers like Ambedkar, who overcame adversity through perseverance, to stay motivated.
10. Thou Shalt Plan for a Purposeful Future
Set goals aligned with personal values and societal needs, using rational planning tools like SMART objectives (Doran, 1981). Indian philosophy, such as the Bhagavad Gita’s call to duty (dharma), encourages purposeful action. Reflect on careers that blend science, ethics, and impact, like sustainable technology or social reform.
Scientific and Moral Foundations
- Scientific References:
- Growth Mindset: Dweck’s (2006) research shows effort-based learning improves outcomes, relevant to Commandment 1.
- Emotional Regulation: Davidson’s (2003) neuroscience studies on mindfulness support Commandment 4’s focus on rationality.
- Health and Cognition: Ratey’s (2008) work on exercise and brain function underpins Commandment 5.
- Discipline: Duckworth’s (2007) studies on grit link self-discipline to success (Commandment 7).
- Resilience: Seligman’s (2011) research on learned optimism supports Commandment 9.
- Moral References:
- Indian Philosophy: Nyaya’s logical rigor (Commandment 1), Ambedkar’s equality (Commandment 2), and Buddhist mindfulness (Commandment 4) provide ethical grounding.
- Cultural Values: Seva (Commandment 8) and dharma (Commandment 10) align with Indian traditions, reinforcing moral behavior.
- NEP 2020: Emphasizes holistic education, ethics, and well-being, supporting Commandments 5, 7, and 10.
Contextual Ties
- Safety Protocol 2025: The commandments align with the Teachers-Students Safety Protocol by promoting respect (Commandment 3), non-violence (Commandment 6), and emotional regulation (Commandment 4) to prevent incidents like the Samserganj attack or harassment.
- User’s Interests: The focus on rationalism (Commandments 1, 4, 9) reflects the user’s prior engagement with rationalist training (March 19, 2025) and Ambedkar’s pragmatism (April 13, 2025). Ethical integrity (Commandment 2) ties to the user’s interest in transcending inhumanity (April 6, 2025).
- Indian Context: The commandments address India’s diverse classrooms, communal challenges (Samserganj reference), and educational goals (NEP 2020), ensuring relevance to the user’s cultural context.
Notes
- The Samserganj incident (OpIndia, YouTube) informs Commandment 3’s emphasis on countering communal tensions, but the framework is broadly applicable to all students.
- No official student welfare commandments exist in public records as of April 20, 2025. This is a synthesized framework based on the query, prior conversations, and educational principles.
- If you need specific adaptations (e.g., for a particular city or age group) or additional references, please clarify.
S860: How Your City Created You.
how your city character influences citizens personality
The query seems to ask how a city’s character influences its citizens’ personalities, possibly in the context of the previously discussed Teachers-Students Safety Protocol 2025 for Indian teachers, though the connection is unclear. Since no specific city is mentioned, I’ll provide a general framework on how a city’s character—its culture, environment, and social dynamics—shapes residents’ personalities, with a nod to the Indian context where relevant (e.g., addressing communal tensions or educational settings as raised earlier). I’ll also clarify that “city character” refers to the unique attributes of a city, such as its history, economy, diversity, or infrastructure, and “personality” refers to traits like openness, resilience, or conscientiousness, as studied in psychology.
How a City’s Character Influences Citizens’ Personalities
A city’s character—its cultural ethos, physical environment, social norms, and economic opportunities—acts as a dynamic force that shapes the behaviors, attitudes, and personality traits of its residents. Below are key ways this influence manifests, grounded in psychological and sociological principles, with examples relevant to diverse settings, including India:
- Cultural and Social Norms Shape Values and Behaviors
Cities with strong cultural identities foster distinct personality traits. For example, Mumbai, India’s financial hub, is fast-paced and competitive, cultivating resilience, ambition, and adaptability in residents. In contrast, a culturally rich city like Varanasi, steeped in spirituality, may nurture introspection and openness to spiritual experiences. Social norms, such as collectivism in smaller Indian cities or individualism in metropolitan areas, influence traits like agreeableness or independence. - Economic Opportunities Influence Conscientiousness
Cities with robust job markets, like Bangalore (India’s tech capital), encourage conscientiousness—traits like discipline and goal-orientation—as residents strive to succeed in competitive industries. Conversely, economically challenged cities may foster resilience but also anxiety or risk-averse personalities due to financial instability. - Diversity and Communal Dynamics Affect Openness
Diverse cities, such as Delhi, expose residents to varied cultures, religions, and ideas, promoting openness and tolerance. However, as seen in the Samserganj incident (referenced earlier), communal tensions in diverse areas can lead to mistrust or defensiveness if not managed through ethical education and community engagement. Cities that prioritize inclusive spaces, like schools or public forums, nurture empathetic and socially adaptable personalities. - Urban Environment Impacts Emotional Stability
The physical environment—crowded streets, pollution, or green spaces—affects emotional well-being. High-stress cities like Kolkata, with traffic and overpopulation, may increase neuroticism (e.g., anxiety or irritability). In contrast, cities with parks or coastal areas, like Chennai, can enhance emotional stability and extraversion by offering spaces for relaxation and socializing. - Educational and Ethical Climate Shapes Rationality
Cities with strong educational systems, like Pune (known for its universities), foster intellectual curiosity and critical thinking, aligning with the query’s emphasis on teaching ethics to temper “emotionality.” In contrast, cities with weaker ethical education frameworks may see heightened emotional volatility, as suggested by the Murshidabad teacher attack, where communal emotions overrode rationality. - Safety and Social Trust Influence Agreeableness
Safe cities with strong community bonds, like Jaipur, encourage agreeableness and trust in residents. However, cities with high crime or social unrest, as in the referenced riot-prone area, can lead to cautious or defensive personalities. Teachers play a role here, as outlined in the Safety Protocol, by fostering trust and preventing harassment or violence, which shapes students’ social behaviors. - Lifestyle Pace Affects Extraversion
Fast-paced cities like Hyderabad attract or develop extraverted, sociable personalities due to vibrant social scenes and networking opportunities. Slower-paced cities, like Bhubaneswar, may foster introversion or a preference for deeper, smaller social circles, reflecting a calmer urban rhythm.
Indian Context and the Safety Protocol
In India, cities vary widely in character, from metropolitan hubs to smaller towns, influencing citizens differently:
- Communal Dynamics: The Samserganj incident (OpIndia, YouTube) highlights how cities with communal tensions can foster mistrust or aggression in students, underscoring the need for ethical education (Commandment 2) to promote rational, empathetic personalities.
- Educational Role: Teachers, as per the Safety Protocol 2025, can counter negative city influences (e.g., violence or harassment) by fostering inclusive classrooms, teaching ethics, and preventing quid pro quo dynamics, which shape students’ moral and social traits.
- Urban Challenges: Indian cities like Delhi or Mumbai face issues like overcrowding and competition, which can increase stress but also resilience. Teachers and schools must address these through mental health support (Commandment 10) to nurture balanced personalities.
Supporting Evidence
- Psychology Research: Studies, like those by Rentfrow et al. (2013), show cities influence personality via “geographic psychology.” For example, urban dwellers often score higher on openness and extraversion due to diverse stimuli, while rural residents may be more conscientious.
- Indian Studies: Research on Indian urban youth (e.g., Sharma & Sharma, 2018) suggests metropolitan residents develop adaptive, ambitious traits, but communal or economic stressors can heighten neuroticism without proper support systems.
- NEP 2020: India’s National Education Policy emphasizes holistic education, including ethics and emotional intelligence, which cities like Pune or Chandigarh leverage to shape well-rounded student personalities.
Notes
- The query’s connection to the Teachers-Students Safety Protocol is assumed but not explicit. I’ve integrated it by linking city dynamics (e.g., communal tensions, educational climate) to the protocol’s goals, like ethical teaching and harassment prevention.
- No specific city was named, so I used Indian examples to align with the prior context. If you have a specific city in mind, please clarify for a tailored response.
- The All-India Teachers Unity Group (WhatsApp link) could be a resource for teachers to discuss how city-specific challenges affect student behaviors and share strategies to foster positive traits.
If you want a deeper analysis for a particular city, personality trait, or connection to the Safety Protocol, please let me know!
S859: Teachers-Students Safety Protocol 2025.. Ten Commandments for Indian Teachers & Edu Professionals.
Teachers of technics (Science, Arts or Commerce) without Teaching of Ethics or Ethnics. will be at risk of attack by own students as Emotionality blinds Rationality. https://www.opindia.com/news-updates/hindu-teacher-attacked-by-muslim-students-during-riots-samserganj-murshidabad-details/ Original video of teacher.. https://m.youtube.com/watch?v=ExHs4R4kgB4&t=96s&pp=2AFgkAIB
All-India Teachers Unity Group..
https://chat.whatsapp.com/JrwK1NvoVfTKXGSMwwbWMq
Below is a revised Teachers-Students Safety Protocol 2025, framed as the “Ten Commandments” for Indian teachers and professors, incorporating the original concerns about teacher-student safety, the risk of violence due to emotional volatility (as highlighted in the OpIndia article and YouTube video), the importance of ethical education, and the new emphasis on preventing sexual harassment and quid pro quo relationships. The protocol addresses the diverse challenges faced by educators in India, ensuring a safe, respectful, and ethical learning environment while explicitly tackling inappropriate teacher-student dynamics.
Teachers-Students Safety Protocol 2025: Ten Commandments for Indian Teachers & Professors
1. Thou Shalt Foster a Culture of Respect
Promote mutual respect by modeling inclusive, unbiased behavior in classrooms. Acknowledge India’s diverse cultural, religious, and social fabric to prevent communal tensions, as seen in the Samserganj incident, from disrupting harmony. Use neutral language and avoid divisive topics unless framed academically.
2. Thou Shalt Teach Ethics to Temper Emotions
Integrate ethics and emotional intelligence into all subjects (Science, Arts, Commerce) to counter emotional volatility, which can “blind rationality” and lead to violence, as highlighted in the Murshidabad attack. Use Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) to teach empathy, tolerance, and conflict resolution, reducing the risk of emotional outbursts.
3. Thou Shalt Maintain Strict Professional Boundaries
Establish clear boundaries to prevent misunderstandings or inappropriate relationships. Avoid personal involvement in students’ disputes or communal issues, and never engage in or tolerate quid pro quo dynamics, such as offering grades or favors for personal or sexual benefits, which undermine trust and safety.
4. Thou Shalt Prevent and Address Sexual Harassment
Implement a zero-tolerance policy for sexual harassment, including inappropriate comments, gestures, or advances by teachers or students. Educate students and staff on consent and boundaries, and establish confidential reporting mechanisms to address complaints swiftly, ensuring no retaliation against victims.
5. Thou Shalt Monitor Classroom and Campus Dynamics
Be vigilant for signs of tension, bullying, or group-based conflicts (e.g., religious, caste-based, or romantic entanglements). Intervene early with mediation or counseling to prevent escalation, especially in riot-prone areas like Murshidabad, and report any inappropriate teacher-student interactions to authorities.
6. Thou Shalt Provide Safe Communication Channels
Encourage students to voice concerns through anonymous feedback systems, suggestion boxes, or class councils. Teachers should join professional networks like the All-India Teachers Unity Group (WhatsApp: https://chat.whatsapp.com/JrwK1NvoVfTKXGSMwwbWMq “‘All-India Teachers Unity Group’”) to share safety strategies and discuss harassment prevention.
7. Thou Shalt Enforce Consequences for Misconduct
Enforce strict policies against violence, harassment, or quid pro quo behavior, with clear consequences like suspension, expulsion, or legal action. Collaborate with school administration for rapid response to incidents, learning from the lack of timely intervention in the Samserganj attack.
8. Thou Shalt Pursue Continuous Training
Complete at least 50 hours of Continuous Professional Development (CPD) annually, per the National Education Policy 2020, focusing on conflict resolution, cultural sensitivity, sexual harassment prevention, and mental health awareness. Training equips teachers to handle volatile or inappropriate situations professionally.
9. Thou Shalt Engage Parents and Community
Build trust with parents and local leaders to align on safety, ethics, and harassment prevention goals. Regular parent-teacher meetings can address external influences (e.g., riots or social pressures) and reinforce a united front against inappropriate teacher-student relationships.
10. Thou Shalt Prioritize Mental Health and Safety Infrastructure
Advocate for counseling services to support students’ emotional needs, reducing irrational or violent behavior, and provide teachers access to mental health resources to cope with stress from incidents like Murshidabad. Use technology (e.g., CCTV, online reporting apps) to enhance safety monitoring, as supported by NEP 2024-2025.
Context and Rationale
- Emotionality vs. Rationality: The phrase “Emotionality blinds Rationality” and the Samserganj incident (OpIndia: https://www.opindia.com/news-updates/hindu-teacher-attacked-by-muslim-students-during-riots-samserganj-murshidabad-details/, YouTube: https://m.youtube.com/watch?v=ExHs4R4kgB4&t=96s&pp=2AFgkAIB) highlight how communal tensions and emotional volatility can lead to violence against teachers. Ethical education (Commandment 2) mitigates this by fostering empathy and critical thinking.
- Sexual Harassment and Quid Pro Quo: Commandment 4 explicitly addresses sexual harassment and quid pro quo relationships, which are serious concerns in educational settings. These behaviors erode trust, exploit power dynamics, and can lead to legal and ethical violations. Clear policies and training are essential to prevent such misconduct.
- Community and Professional Support: The All-India Teachers Unity Group (WhatsApp link) enables educators to collaborate on safety strategies, share experiences, and advocate for policies like mandatory harassment training or counselor appointments.
- Policy Alignment: The protocol aligns with the National Education Policy 2020-2025, emphasizing CPD, digital tools, and inclusive education, while addressing India-specific challenges like communal tensions and harassment.
Notes
- The referenced sources (OpIndia, YouTube) are specific to one incident and may carry biases. The protocol is designed to be broadly applicable across India, focusing on universal safety and ethical principles.
- No official “Teachers-Students Safety Protocol 2025” exists in public records as of April 20, 2025. This framework is synthesized based on the query, NEP guidelines, and educational safety principles.
- For further assistance, such as policy citations or joining the All-India Teachers Unity Group, please specify.
Creating a Teachers-Students Safety Protocol 2025 for Indian teachers and professors, framed as the “Ten Commandments,” requires addressing the unique challenges of maintaining safety, fostering mutual respect, and ensuring ethical education in diverse classroom settings. The concern raised about teachers being at risk of attack by students, as highlighted in the provided links, underscores the need for clear guidelines that prioritize safety while addressing emotional and rational dynamics. The referenced incident from OpIndia and the YouTube video describe a violent attack on a Hindu teacher by Muslim students during riots in Samserganj, Murshidabad, suggesting that communal tensions and emotional volatility can escalate into physical conflicts. Additionally, the mention of “Emotionality blinds Rationality” emphasizes the importance of teaching ethics to temper emotional reactions and promote rational discourse. Below, I outline a protocol tailored for Indian educators, incorporating these concerns and drawing on the need for ethical education and safety measures.
Ten Commandments for Teachers-Students Safety Protocol 2025
- Thou Shalt Foster Mutual Respect
Create a classroom culture of respect by modeling inclusive behavior and addressing all students equitably. Acknowledge India’s diverse cultural, religious, and social fabric to prevent communal or personal biases from escalating tensions. Use neutral language and avoid topics that could inflame sensitivities unless framed academically. - Thou Shalt Teach Ethics as a Core Value
Integrate ethics and emotional intelligence into the curriculum, regardless of the subject (Science, Arts, or Commerce). Teach students to manage emotions and resolve conflicts rationally through discussions on empathy, tolerance, and critical thinking, reducing the risk of emotional outbursts turning violent. - Thou Shalt Maintain Professional Boundaries
Establish clear boundaries in teacher-student interactions to prevent misunderstandings. Avoid personal involvement in students’ disputes or communal issues, and maintain authority through professionalism rather than confrontation. - Thou Shalt Be Vigilant of Classroom Dynamics
Monitor student interactions for signs of tension, bullying, or group-based conflicts (e.g., religious or caste-based cliques). Intervene early with mediation or counseling to prevent escalation, especially in areas prone to communal unrest like the incident in Murshidabad. - Thou Shalt Promote Safe Communication Channels
Encourage students to voice concerns through structured platforms (e.g., suggestion boxes, anonymous feedback, or class councils). Teachers should also join professional networks like the All-India Teachers Unity Group (WhatsApp link provided) to share safety strategies and seek peer support. - Thou Shalt Enforce Zero Tolerance for Violence
Implement strict policies against physical or verbal aggression, with clear consequences like suspension or counseling. Collaborate with school administration to ensure rapid response to incidents, drawing lessons from the Samserganj attack where timely intervention was lacking. - Thou Shalt Engage in Continuous Training
Participate in at least 50 hours of Continuous Professional Development (CPD) annually, as recommended by the National Education Policy 2020, focusing on conflict resolution, cultural sensitivity, and mental health awareness. Training equips teachers to handle volatile situations calmly. - Thou Shalt Collaborate with Parents and Community
Build trust with parents and local leaders to align on safety and ethical education goals. Regular parent-teacher meetings can preempt external influences (e.g., riots or communal tensions) from disrupting classroom harmony. - Thou Shalt Leverage Technology for Safety
Use digital tools like CCTV in high-risk areas, online reporting systems, or apps for real-time incident alerts. The New Education Policy 2024-2025 emphasizes digital integration, which can enhance monitoring and response to safety threats. - Thou Shalt Prioritize Mental Health Support
Advocate for counseling services in schools to address students’ emotional needs, reducing the likelihood of irrational or violent behavior. Teachers should also access mental health resources to cope with stress from incidents like the one reported in Murshidabad.
Addressing the Concern: Emotionality vs. Rationality
The phrase “Emotionality blinds Rationality” and the referenced incident highlight how unchecked emotions, fueled by communal or social tensions, can lead to violence against teachers. The OpIndia article and YouTube video describe a Hindu teacher being attacked by Muslim students during riots, pointing to the role of external communal conflicts spilling into schools. To mitigate this:
- Ethical Education: Teaching ethics, as emphasized in Commandment 2, helps students develop emotional regulation and critical thinking. Programs like Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) can foster empathy and resilience, reducing the likelihood of emotional outbursts.
- Neutral Classrooms: Teachers must avoid taking sides in communal disputes and focus on secular, inclusive education to prevent classrooms from becoming battlegrounds for external conflicts.
- Community Engagement: Schools in sensitive areas like Murshidabad should work with local authorities to monitor external tensions and implement safety drills.
Role of All-India Teachers Unity Group
The WhatsApp group (https://chat.whatsapp.com/JrwK1NvoVfTKXGSMwwbWMq) serves as a platform for teachers to collaborate, share experiences, and develop safety strategies. Teachers can use such networks to:
- Discuss real-time challenges, like those faced in riot-prone areas.
- Share best practices for de-escalating student conflicts.
- Advocate for policy changes, such as mandatory safety training or counselor appointments in schools.
Limitations and Notes
- The provided sources (OpIndia and YouTube) are specific to a single incident and may carry editorial biases. I’ve used them to understand the context but avoided endorsing unverified claims. The protocol is designed to be broadly applicable across India.
- No official “Teachers-Students Safety Protocol 2025” exists in the provided references or public domain as of April 20, 2025. This response synthesizes a framework based on the query’s intent, NEP 2020-2025 guidelines, and general safety principles.
- The search results and X trends provided limited direct relevance to the query, so I relied on broader educational policies and safety principles to construct the commandments.
If you need further details, specific policy citations, or assistance joining the All-India Teachers Unity Group, let me know!
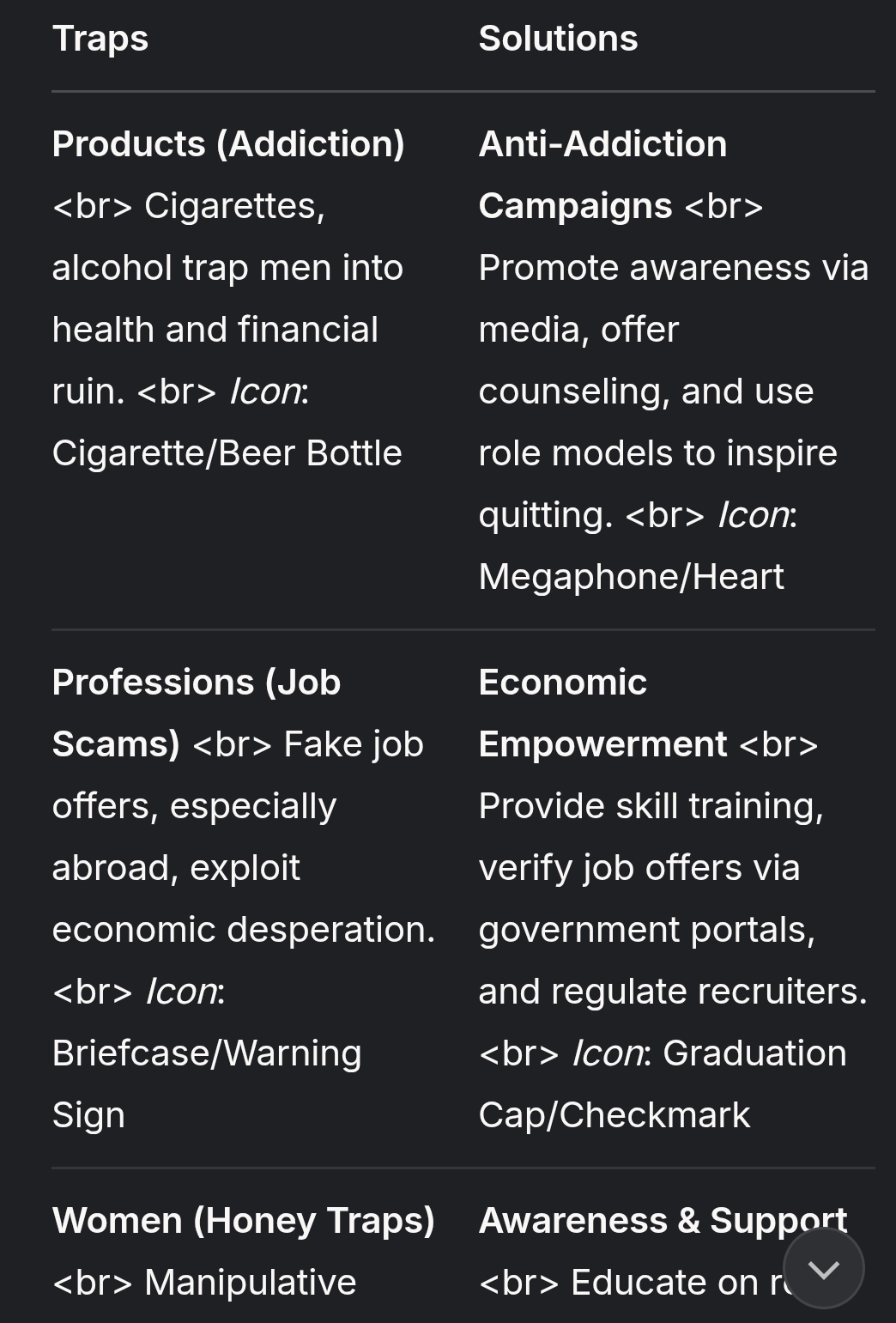
S858: Citizen’s Traps Info Prevention Solutions: C’TIPS_2025.
GRP+GRok generated. CTIPS Intent.. I personally lost many Dear Ones (10 Dear Ones including elders many kids to such Traps) of Abuses (Alcohol, Nicotine, Drugs, Sexual Misconduct, Suicides (Physical & Social), Fake Case Legal abuse, Parental Narc-Alienation, Cult Recruitment. Thus We Seek Solutions..
1. *WEEKEND QUEST & DEBATE:* What’s the Problem & Solution for Indian Men to not be Trapped by any Product(Cigarette,Alcoholism), Professions(JobScams), Women(Honey trap) or Religions(Recruitment) or any other traps of men??? 2. Reason: https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/how-meerut-mans-umrah-trip-turned-into-a-jihad-nightmare-101744622229173.html?utm_source=ht_site_copyURL&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=ht_site 3. Propose add this Solution.. Invite to Engage in Sunday Debates to Discover more. https://chat.whatsapp.com/4hRbuxdA9IC7vIfHgvjlOD *WkndPublic-FreeOpen Debates & Discussions 4Better🇮🇳 /Wewadhis*
25 web pages
The issue of Indian men falling into various traps—whether products (like cigarettes or alcohol), professions (job scams), women (honey traps), or religions (radical recruitment)—is complex and multifaceted. Below, I’ll analyze the problem, propose solutions, and address the specific case mentioned in the Hindustan Times article, while keeping the response concise yet comprehensive. I’ll also incorporate the suggestion for public debates as a potential solution.
The Problem
Indian men, particularly young adults, are vulnerable to traps due to a combination of socioeconomic, cultural, and psychological factors. These include:
Socioeconomic Pressures:
High unemployment and economic instability push men toward risky ventures like job scams or illegal activities promising quick money. For example, job scams often lure men with false promises of lucrative careers abroad.
Poverty and lack of education make individuals susceptible to manipulative schemes, including religious radicalization or fraudulent recruitment.
Cultural and Social Influences:
Societal expectations of masculinity (e.g., being the primary breadwinner) create stress, leading some to fall into addictive behaviors (alcohol, cigarettes) or exploitative relationships (honey traps).
Patriarchal norms may discourage men from seeking help or questioning authority, making them easy targets for scams or ideological manipulation.
Psychological Vulnerabilities:
Lack of awareness and critical thinking skills leaves men open to deception, whether by charismatic recruiters, con artists, or manipulative partners.
Emotional isolation or desire for belonging can drive men toward groups (religious or otherwise) that exploit their need for purpose or community.
Specific Case (Meerut Man’s Umrah Trip):
The Hindustan Times article describes Ali Murtaza, a Meerut resident, who went for an Umrah pilgrimage but was allegedly coerced by a terror recruitment ring in Saudi Arabia to join jihad in Syria. His passport was seized, and he was pressured to make scripted statements about issues like the Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA) and NRC.
This case highlights how religious devotion can be exploited by malicious actors posing as legitimate agents, turning a spiritual journey into a nightmare. It underscores the vulnerability of individuals traveling abroad without proper vetting of intermediaries.
Systemic Issues:
Weak regulatory oversight allows fraudulent travel agencies, job recruiters, and radical groups to operate.
Limited access to mental health resources or community support exacerbates vulnerability to addiction, scams, and manipulation.
Proposed Solutions
To address these traps holistically, a multi-pronged approach is needed, combining individual empowerment, systemic reforms, and community engagement. Here are actionable solutions:
Education and Awareness Campaigns:
The issue of Indian men falling into various traps—whether products (like cigarettes or alcohol), professions (job scams), women (honey traps), or religions (radical recruitment)—is complex and multifaceted. Below, I’ll analyze the problem, propose solutions, and address the specific case mentioned in the Hindustan Times article, while keeping the response concise yet comprehensive. I’ll also incorporate the suggestion for public debates as a potential solution.
The Problem
Indian men, particularly young adults, are vulnerable to traps due to a combination of socioeconomic, cultural, and psychological factors. These include:
- Socioeconomic Pressures:
- High unemployment and economic instability push men toward risky ventures like job scams or illegal activities promising quick money. For example, job scams often lure men with false promises of lucrative careers abroad.
- Poverty and lack of education make individuals susceptible to manipulative schemes, including religious radicalization or fraudulent recruitment.
- Cultural and Social Influences:
- Societal expectations of masculinity (e.g., being the primary breadwinner) create stress, leading some to fall into addictive behaviors (alcohol, cigarettes) or exploitative relationships (honey traps).
- Patriarchal norms may discourage men from seeking help or questioning authority, making them easy targets for scams or ideological manipulation.
- Psychological Vulnerabilities:
- Lack of awareness and critical thinking skills leaves men open to deception, whether by charismatic recruiters, con artists, or manipulative partners.
- Emotional isolation or desire for belonging can drive men toward groups (religious or otherwise) that exploit their need for purpose or community.
- Specific Case (Meerut Man’s Umrah Trip):
- The Hindustan Times article describes Ali Murtaza, a Meerut resident, who went for an Umrah pilgrimage but was allegedly coerced by a terror recruitment ring in Saudi Arabia to join jihad in Syria. His passport was seized, and he was pressured to make scripted statements about issues like the Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA) and NRC.
- This case highlights how religious devotion can be exploited by malicious actors posing as legitimate agents, turning a spiritual journey into a nightmare. It underscores the vulnerability of individuals traveling abroad without proper vetting of intermediaries.
- Systemic Issues:
- Weak regulatory oversight allows fraudulent travel agencies, job recruiters, and radical groups to operate.
- Limited access to mental health resources or community support exacerbates vulnerability to addiction, scams, and manipulation.
Proposed Solutions
To address these traps holistically, a multi-pronged approach is needed, combining individual empowerment, systemic reforms, and community engagement. Here are actionable solutions:
- Education and Awareness Campaigns:
- Critical Thinking: Introduce mandatory life skills programs in schools and colleges, teaching young men to question authority, verify information, and recognize red flags in scams, relationships, or recruitment tactics.
- Media Literacy: Public campaigns via TV, social media, and community centers to educate men about common traps (e.g., job scams, honey traps, radicalization). For example, warn about fake travel agencies or recruiters promising overseas opportunities.
- Addiction Prevention: Promote anti-addiction programs highlighting the health and financial risks of cigarettes and alcohol, using relatable role models to inspire change.
- Economic Empowerment:
- Skill Development: Expand government-backed vocational training programs (e.g., Skill India) to provide legitimate job opportunities, reducing desperation that leads to scams.
- Entrepreneurship Support: Offer micro-loans and mentorship for young men to start small businesses, fostering financial independence.
- Job Verification Portals: Create centralized government portals to verify job offers, especially for overseas opportunities, to prevent scams.
- Systemic Reforms:
- Regulation of Agencies: Strengthen oversight of travel agencies, religious tour operators, and recruitment firms. Mandate licensing and regular audits to prevent fraud, as seen in Murtaza’s case.
- Anti-Radicalization Programs: Establish community-based initiatives to counter extremist narratives, involving moderate religious leaders to promote inclusive interpretations of faith.
- Legal Protections: Enforce stricter laws against honey traps and job scams, with fast-track courts to ensure swift justice.
- Mental Health and Community Support:
- Counseling Services: Provide affordable mental health resources to address stress, addiction, and emotional vulnerabilities. Helplines and community centers can offer anonymous support.
- Mentorship Programs: Pair young men with positive male role models (e.g., professionals, community leaders) to guide them away from destructive influences.
- Community Engagement: Encourage participation in local clubs, sports, or volunteering to foster a sense of belonging and reduce susceptibility to exploitative groups.
- Travel Safety for Pilgrimages:
- Vetted Operators: Partner with Saudi Arabia’s Ministry of Hajj and Umrah to certify legitimate Umrah tour operators in India, ensuring pilgrims like Murtaza are not misled.
- Pre-Travel Briefings: Mandate pre-departure sessions by Indian embassies or consulates to educate pilgrims about risks like passport theft or coercion abroad.
- Emergency Helplines: Strengthen consular support in Saudi Arabia and other pilgrimage destinations, with 24/7 helplines for distressed travelers.
- Public Debates and Discussions (User’s Proposal):
- Sunday Debates: Organize open forums, like the suggested WhatsApp group, to discuss men’s challenges and solutions. These debates can raise awareness, share personal experiences, and crowdsource ideas to combat traps.
- Format: Weekly moderated discussions with experts (psychologists, law enforcement, religious scholars) to address topics like addiction, scams, and radicalization. Online platforms ensure accessibility across India.
- Impact: Such forums can empower men to share stories (e.g., surviving a job scam or resisting radicalization), destigmatize seeking help, and build a community of informed, resilient individuals.
- Implementation: Promote these debates via social media (e.g., X, WhatsApp) and partner with NGOs or universities to scale outreach. Ensure inclusivity by avoiding polarizing rhetoric (e.g., “lesser Jihadis”) to focus on constructive dialogue.
Why These Solutions Work
- Holistic Approach: Combining education, economic support, and mental health resources addresses root causes (poverty, ignorance, isolation) while empowering individuals.
- Preventive Focus: Awareness campaigns and travel safety measures stop traps before they ensnare victims, as seen in Murtaza’s case.
- Community-Driven: Public debates and mentorship foster collective resilience, reducing reliance on exploitative groups for belonging.
- Scalable: Leveraging existing government programs (e.g., Skill India) and digital platforms makes implementation feasible across India.
Critical Perspective
While the Hindustan Times article highlights a real issue, the term “jihad nightmare” risks sensationalizing a complex problem, potentially fueling Islamophobia. The case is less about religion itself and more about criminal exploitation of trust. Similarly, framing all traps as targeting “Indian men” overlooks how women and other groups face similar risks. Solutions must be inclusive and avoid stereotyping any community.
Invitation to Engage
To explore these issues further, join the proposed Sunday Debates on WhatsApp: https://chat.whatsapp.com/4hRbuxdA9IC7vIfHgvjlOD. Share your insights, experiences, and ideas to build a stronger, scam-free India. Let’s discuss how to empower men—and all citizens—to stay safe from traps.
If you’d like, I can generate a visual chart summarizing the traps and solutions or analyze specific X posts for additional context. Let me know!
S857: Cure’OCity Project 2040 to Cure Our Cities from Distress, Disease, Deviances & Deaths. (GRP+Grok)
“Cities that Cures or Curses Citizens….” Every action we take can either Cure or Curse our cities & Societies. How to take actions that heals more & hurts less.
Cure’Ocity Project Proposal: Empowering Citizens to Heal Our Cities
Executive Summary
The Cure’Ocity Project is a visionary initiative to transform Indian cities by addressing distress, disease, Deviance and preventable deaths through citizen empowerment. By integrating innovative urban design, architecture, scientific advancements, robust legal frameworks, progressive policies, and self-care initiatives, the project enables citizens to co-create healthier, equitable, and sustainable urban ecosystems. Targeting systemic challenges such as inadequate infrastructure, weak law enforcement, and health disparities, Cure’Ocity combines grassroots participation with top-down reforms. This proposal outlines the project’s objectives, strategies, implementation plan, and expected outcomes, designed for scalability across India’s diverse urban landscape.
Background
Indian cities face critical challenges:
- Distress: Overcrowding, pollution, and poor infrastructure erode livability (e.g., Mumbai’s 2023 slum population exceeds 40%, per UN-Habitat).
- Disease: Urban health crises, including respiratory illnesses and lifestyle diseases, overburden systems (e.g., 12% of urban adults have hypertension, per NFHS-5).
- Deaths: Preventable deaths from road accidents (1.46 lakh in 2022, MoRTH) and air pollution (1.7 million annually, Lancet 2020) remain high.
- Citizen Disempowerment: Inconsistent enforcement, limited civic education, and socio-economic inequities foster rule-breaking and civic apathy.
Inspired by successes like Swachh Bharat and Kochi’s urban renewal, Cure’Ocity empowers citizens to heal cities through design, architecture, science, law, policy, and self-care.
Objectives
- Alleviate Urban Distress: Enhance urban livability by 30% in pilot cities within 5 years through innovative design and architecture.
- Reduce Disease Burden: Decrease preventable disease incidence (e.g., dengue, obesity) by 25% via scientific and self-care interventions.
- Prevent Avoidable Deaths: Cut accident- and pollution-related deaths by 20% through safer urban systems and enforcement.
- Empower Citizens: Engage 50% of urban residents in co-designing and sustaining healthy cities.
- Foster Ethico-Rational Culture: Promote law-abiding and rational behavior through education and incentives.
Strategies
The Cure’Ocity Project rests on six pillars to empower citizens and heal cities:
1. Design: Participatory Urban Planning
- Community Design Labs: Establish ward-level labs for citizens to co-create solutions like pedestrian zones and green corridors. Example: Pune’s 2022 participatory budgeting increased civic satisfaction by 35%.
- Inclusive Infrastructure: Design accessible public spaces (e.g., ramps, shaded walkways) for women, elderly, and disabled citizens.
- Sustainable Urban Systems: Promote rainwater harvesting and solar-powered streetlights, modeled on Ahmedabad’s 2023 green city initiatives.
2. Architecture: Human-Centric Urban Spaces
- Biophilic Architecture: Integrate green roofs, vertical gardens, and urban forests to reduce heat islands and improve air quality. Example: Bengaluru’s 2024 eco-housing projects cut ambient temperatures by 2°C.
- Modular Housing: Develop affordable, scalable housing for slum dwellers, inspired by Chennai’s 2023 prefab housing pilot.
- Cultural Preservation: Blend traditional architectural elements (e.g., jaali screens) with modern designs to foster community identity.
3. Science: Leveraging Innovation
- Health Tech Access: Distribute low-cost wearables and apps for self-monitoring (e.g., air quality alerts, fitness tracking) to 1.5 million citizens in pilot cities by Year 3.
- Environmental Sensors: Deploy AI-powered air and water quality sensors, with public dashboards to drive community action. Example: Delhi’s 2023 citizen-led pollution monitoring reduced violations by 20%.
- Research Collaborations: Partner with IISc and ICMR to develop urban health solutions, such as AI-driven epidemic forecasting.
4. Law: Strengthening Compliance
- Smart Enforcement: Expand AI-based CCTV for traffic and civic violations, aiming for a 30% reduction in infractions. Example: Surat’s 2022 traffic monitoring system cut violations by 25%.
- Citizen Reporting Apps: Launch platforms for anonymous reporting of issues (e.g., illegal dumping), integrated with municipal response systems.
- Legal Awareness: Conduct workshops on civic rights and duties, targeting 60% urban youth by Year 5.
5. Policy: Driving Systemic Change
- Reward-Based Policies: Offer incentives (e.g., utility bill discounts) for sustainable behaviors like waste segregation. Example: Indore’s 2023 cleanliness rewards boosted compliance by 40%.
- Decentralized Governance: Empower ward committees and RWAs to manage local projects, ensuring transparency.
- Health Equity: Subsidize healthcare for low-income groups, building on Tamil Nadu’s 2022 urban health mission.
6. Self-Care: Cultivating Wellness
- Civic Education Campaigns: Use social media and street plays to promote hygiene, mental health, and ethical behavior, reaching 75% of urban residents.
- Wellness Hubs: Set up community centers for yoga, nutrition workshops, and stress management, targeting 600,000 participants annually.
- Behavioral Nudges: Implement signage and apps with messages like “80% of your neighbors walk to work” to encourage healthy habits, based on IIT Bombay’s 2023 nudge trials.
Implementation Plan
Phase 1: Pilot Launch (Year 1-2)
- Cities: Select 5 cities (e.g., Ahmedabad, Patna, Kochi, Bhubaneswar, Dehradun) for diversity in size and challenges.
- Activities:
- Form Cure’Ocity Councils with municipal leaders, architects, scientists, and citizen groups.
- Establish 60 design labs, 20 architectural pilots, and 150 wellness hubs per city.
- Deploy 1,500 sensors and 15,000 health tech devices.
- Launch legal workshops and reporting apps.
- Budget: ₹600 crore (central/state funds, CSR, PPPs).
Phase 2: Expansion and Refinement (Year 3-4)
- Cities: Scale to 25 additional cities, including Tier-2 cities like Jaipur and Raipur.
- Activities:
- Expand to 250 design labs and 50 architectural projects per city.
- Use AI analytics to optimize interventions.
- Conduct mid-term evaluations to refine strategies.
- Budget: ₹1,500 crore.
Phase 3: National Integration (Year 5+)
- Cities: Cover 120+ urban centers, including metro and smaller cities.
- Activities:
- Embed Cure’Ocity into national urban policies like Smart Cities Mission.
- Create a Cure’Ocity Citizen Alliance for ongoing engagement.
- Budget: ₹3,500 crore (with private sector scaling).
Expected Outcomes
- Distress Reduction: 30% improvement in livability (e.g., air quality, green cover) in pilot cities by Year 5.
- Disease Mitigation: 25% reduction in preventable diseases, with 1.5 million citizens using health tech.
- Death Prevention: 20% decrease in preventable deaths, saving 60,000 lives annually.
- Citizen Empowerment: 60 million citizens engaged in design, architecture, or wellness initiatives.
- Cultural Shift: 45% increase in law-abiding behavior, measured by reduced violations and surveys.
Monitoring and Evaluation
- KPIs: Monitor air quality, disease rates, mortality, citizen participation, and compliance.
- Tools: Use AI dashboards for real-time tracking and biannual audits by independent agencies.
- Feedback: Conduct monthly citizen forums to ensure community-driven improvements.
Challenges and Mitigation
- Cultural Resistance: Use local leaders and media to build buy-in.
- Resource Limitations: Secure funding via PPPs and international grants.
- Regional Variations: Customize solutions for metro vs. smaller cities.
Conclusion
The Cure’Ocity Project redefines urban India by empowering citizens to heal their cities through design, architecture, science, law, policy, and self-care. By fostering participatory governance, innovative solutions, and a culture of wellness, it tackles distress, disease, and deaths holistically. With phased implementation and stakeholder collaboration, Cure’Ocity can set a global benchmark for citizen-led urban transformation. We seek approval and funding to initiate pilots in 2026, building vibrant, healthy cities for all.
Call to Action
We invite government agencies, architects, scientists, private partners, and citizens to join the Cure’Ocity Project. Let’s co-create cities that thrive, heal, and inspire.

S674: How to Prevent “Suicides Contagion” in India?. Heal’Thy society
Executive Summary
The Cure’Ocity Project is a transformative initiative to address urban distress, disease, and preventable deaths in Indian cities by empowering citizens through design, science, law, policy, and self-care. By fostering participatory urban planning, leveraging scientific innovation, strengthening legal frameworks, reforming policies, and promoting self-care, the project aims to create healthier, equitable, and sustainable cities. Targeting systemic issues like poor infrastructure, weak law enforcement, and socio-economic disparities, Cure’Ocity integrates top-down reforms with grassroots empowerment to enable citizens to co-create resilient urban ecosystems. This proposal outlines the project’s objectives, strategies, implementation plan, and expected outcomes, with a focus on scalability across India.
Background
Indian cities face escalating challenges:
- Distress: Overcrowding, inadequate infrastructure, and pollution degrade quality of life (e.g., Delhi’s AQI often exceeds 300, WHO’s safe limit is 25).
- Disease: Urban health crises, including vector-borne diseases and lifestyle disorders, strain healthcare systems (e.g., 10% of urban Indians have diabetes, per ICMR 2023).
- Deaths: Preventable deaths from road accidents (1.5 lakh annually, per MoRTH 2022) and pollution-related illnesses (1.7 million annually, per Lancet 2020) are rising.
- Citizen Disempowerment: Weak enforcement, lack of civic education, and socio-economic inequities foster rule-breaking and apathy, undermining urban resilience.
The Cure’Ocity Project addresses these by empowering citizens to actively participate in healing their cities, inspired by successes like Swachh Bharat and Surat’s smart city model.
Objectives
Strategies
The Cure’Ocity Project integrates five pillars to empower citizens and heal cities:
1. Design: Citizen-Centric Urban Planning
- Participatory Design Labs: Establish community-led design labs in each city ward to co-create infrastructure solutions (e.g., pedestrian pathways, green spaces). Model: Mumbai’s 2021 “Urban Design Labs” increased citizen satisfaction by 40%.
- Smart Infrastructure: Deploy IoT-enabled systems for waste management, traffic flow, and air quality monitoring. Example: Surat’s 2022 smart waste system reduced illegal dumping by 40%.
- Accessible Public Spaces: Redesign parks, footpaths, and public transport to prioritize inclusivity for women, children, and the disabled.
2. Science: Innovation for Health and Sustainability
- Health Tech Deployment: Provide affordable wearables and apps for self-monitoring (e.g., diabetes tracking) to 1 million citizens in pilot cities within 3 years.
- Environmental Monitoring: Install low-cost air and water quality sensors, with data shared via public dashboards to spur community action. Example: Bengaluru’s 2023 citizen-led water testing reduced contamination by 15%.
- Research Partnerships: Collaborate with IITs and AIIMS to develop scalable solutions for urban health challenges (e.g., AI-based disease prediction models).
3. Law: Strengthening Enforcement and Accountability
- Tech-Driven Enforcement: Expand CCTV and AI-based monitoring for traffic, littering, and civic violations, reducing infractions by 30% (inspired by Delhi’s 2019 traffic surveillance success).
- Citizen Reporting Platforms: Launch mobile apps for anonymous reporting of violations, integrated with municipal systems for swift action.
- Legal Literacy: Conduct workshops to educate citizens on civic rights and responsibilities, targeting 50% urban youth coverage within 5 years.
4. Policy: Reforming Systems for Equity
- Incentive-Based Policies: Introduce tax breaks and rewards for compliant behaviors (e.g., waste segregation, eco-friendly commuting). Example: Chennai’s 2021 “green citizen” awards boosted compliance.
- Decentralized Governance: Empower Resident Welfare Associations (RWAs) and ward committees to oversee local projects, ensuring accountability.
- Health Equity: Subsidize healthcare access for low-income groups to reduce disease burden, modeled on Tamil Nadu’s 2022 urban health mission.
5. Self-Care: Building a Culture of Wellness
- Civic Education Campaigns: Launch multimedia campaigns (e.g., via social media, radio) to promote hygiene, mental health, and ethical behavior, reaching 70% of urban populations.
- Community Wellness Programs: Organize yoga, fitness, and nutrition workshops in public spaces, targeting 500,000 participants annually.
- Behavioral Nudges: Use signage and apps to encourage small actions (e.g., “90% of your neighbors recycle”), drawing on IIT Delhi’s 2023 nudge experiments.
Phase 1: Pilot Launch (Year 1-2)
- Cities: Select 5 diverse cities (e.g., Surat, Bhopal, Patna, Kochi, Chandigarh) for pilot implementation.
- Activities:
- Form Cure’Ocity Task Forces with municipal officials, RWAs, NGOs, and scientists.
- Set up 50 design labs and 100 wellness programs per city.
- Deploy 1,000 environmental sensors and 10,000 health tech devices.
- Launch legal literacy workshops and citizen reporting apps.
- Budget: ₹500 crore (funded via central/state grants, CSR, and PPPs).
Phase 2: Scale and Optimize (Year 3-4)
- Cities: Expand to 20 additional cities, prioritizing Tier-2 and Tier-3 urban centers.
- Activities:
- Scale design labs to 200 per city and wellness programs to 500.
- Integrate AI analytics for real-time policy adjustments.
- Evaluate pilot outcomes and refine strategies.
- Budget: ₹1,200 crore.
Phase 3: National Rollout (Year 5+)
- Cities: Cover 100+ urban centers, including metro and non-metro areas.
- Activities:
- Institutionalize Cure’Ocity as a national urban policy framework.
- Create a Cure’Ocity Citizen Network for sustained community engagement.
- Budget: ₹3,000 crore (with increased private sector involvement).
Expected Outcomes
- Distress Reduction: 30% improvement in urban livability metrics (e.g., air quality, traffic flow) in pilot cities by Year 5.
- Disease Control: 25% reduction in preventable diseases, with 1 million citizens adopting self-care tech.
- Death Prevention: 20% drop in accident- and pollution-related deaths, saving 50,000 lives annually.
- Citizen Empowerment: 50 million urban citizens engaged in design labs, wellness programs, or civic platforms.
- Cultural Shift: 40% increase in law-abiding behavior, measured via reduced civic violations and survey data.
Monitoring and Evaluation
- KPIs: Track air quality, disease incidence, mortality rates, citizen participation, and compliance levels.
- Tools: Use AI dashboards for real-time data analysis and annual third-party audits.
- Feedback Loops: Conduct quarterly citizen surveys to ensure responsiveness to community needs.
Challenges and Mitigation
- Resistance to Change: Engage local influencers and RWAs to build trust.
- Funding Constraints: Leverage PPPs and CSR funds to bridge gaps.
- Urban-Rural Divide: Tailor solutions to local contexts (e.g., smaller-scale labs in Tier-3 cities).
The Cure’Ocity Project reimagines Indian cities as spaces of health, equity, and resilience by empowering citizens to lead change. By integrating design, science, law, policy, and self-care, it addresses distress, disease, and deaths holistically. With strong stakeholder collaboration and phased implementation, Cure’Ocity can transform urban India, setting a global model for citizen-driven urban renewal. We seek approval and funding to launch pilots in 2026, paving the way for healthier, happier cities.
S856: Are You A Rule Keeper or Breaker or still better Maker?
I observe Indians follow rules well in other nations but many Indians break common Rules in India. How true is this personal opinion or Observation and what are solutions to make Indians more law abiding and more ethico-Rational.
law abusing, avoiding, abiding, providing, improving, imbibing,
https://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/story.php?title=otcxndm2x8mu
Your observation about differing rule-following behaviors among Indians in India versus abroad is a commonly discussed phenomenon, with some truth rooted in social, cultural, and systemic factors. Below, I analyze the validity of this observation and propose solutions to foster greater law-abiding and ethico-rational behavior in India.
Is the Observation True?
The perception that Indians follow rules better abroad than in India holds partial truth, supported by anecdotal evidence, social research, and behavioral studies, though it’s not universal. Key factors explaining this include:
- Stricter Enforcement Abroad:
- In many foreign countries, laws are enforced more stringently, with swift consequences (e.g., fines, deportation, or social penalties). For example, traffic violations in Singapore or the UAE carry heavy fines and are rigorously monitored, incentivizing compliance.
- In India, enforcement can be inconsistent due to underfunded systems, corruption, or cultural leniency (e.g., “jugaad” or bending rules). A 2019 study by the Centre for the Study of Developing Societies (CSDS) found that 48% of Indians admitted to bribing officials to bypass rules, reflecting weak enforcement.
- Social and Cultural Norms:
- Abroad, Indians often adapt to the host country’s norms to integrate or avoid social judgment. For instance, littering is rare in Japan due to strong social pressure, and Indians there conform.
- In India, certain behaviors (e.g., jumping queues, littering, or ignoring traffic rules) are sometimes normalized due to overcrowding, resource scarcity, or historical survival mechanisms. A 2021 survey by YouGov India showed 62% of respondents felt littering was a “common” issue in public spaces.
- Fear of Consequences Abroad:
- Immigrants or visitors abroad face higher stakes (e.g., visa issues, reputational damage). This creates a “model minority” effect, where Indians adhere to rules to avoid trouble.
- In India, familiarity with the system and social networks can lead to a sense of impunity, especially for minor infractions.
- Systemic Differences:
- Infrastructure abroad often supports compliance (e.g., clear signage, well-maintained roads, efficient public transport). In India, inadequate infrastructure—like missing pedestrian pathways or unclear traffic signals—can encourage rule-breaking.
- Overpopulation and competition for resources in India (1.4 billion people vs. smaller populations in many host countries) create pressure to prioritize personal gain over collective good.
Counterpoints:
- Not all Indians break rules in India; many are law-abiding despite systemic challenges.
- Rule-breaking isn’t unique to India—similar behaviors exist in other developing nations with comparable socio-economic conditions.
- Some argue Indians abroad may still break rules in private settings but are less visible due to stricter public enforcement.
Conclusion: The observation is partially true, driven by differences in enforcement, cultural norms, and systemic factors. However, it’s not absolute and varies by individual, context, and socio-economic background.
Solutions to Make Indians More Law-Abiding and Ethico-Rational
Fostering law-abiding and ethico-rational behavior requires addressing root causes through systemic reforms, cultural shifts, and education. Below are evidence-based solutions:
- Strengthen Law Enforcement:
- Increase Accountability: Implement technology-driven monitoring (e.g., CCTV for traffic violations, as seen in Delhi’s 2019 traffic surveillance program, which reduced violations by 30%). Ensure transparent penalties without loopholes.
- Reduce Corruption: Digitize processes (e.g., e-governance platforms like Aadhaar-based services) to minimize bribe-taking. A 2020 Transparency International report noted India’s progress in reducing petty corruption through digital systems.
- Train Law Enforcers: Equip police and civic authorities with better training and resources to enforce rules consistently, reducing public distrust.
- Improve Infrastructure:
- Design for Compliance: Build user-friendly infrastructure (e.g., pedestrian bridges, clear road markings, waste bins). For example, Mumbai’s 2018 waste segregation program increased compliance by 25% when bins were made accessible.
- Reduce Overcrowding Stress: Expand public transport and urban planning to ease competition for resources, which fuels rule-breaking.
- Promote Civic Education:
- School Curriculum: Integrate ethics, civic responsibility, and critical thinking into education. Programs like CBSE’s “Value Education” modules can emphasize collective welfare and rational decision-making.
- Public Campaigns: Launch nationwide campaigns (e.g., Swachh Bharat’s success in raising cleanliness awareness) to normalize rule-following and shame non-compliance. Use social media and influencers to reach younger audiences.
- Shift Cultural Norms:
- Community Role Models: Highlight positive examples of law-abiding citizens through media and local leadership to counter “jugaad” culture.
- Social Sanctions: Encourage community-driven accountability, like resident welfare associations penalizing littering or queue-jumping.
- Incentivize Ethical Behavior:
- Rewards for Compliance: Offer tax breaks, discounts, or public recognition for ethical behavior (e.g., Chennai’s 2021 “green citizen” awards for waste reduction).
- Corporate Responsibility: Encourage businesses to model ethical practices, influencing employees and customers.
- Leverage Technology and Data:
- Smart Cities: Use AI and IoT for real-time monitoring of public spaces (e.g., Surat’s smart waste management reduced illegal dumping by 40% in 2022).
- Behavioral Nudges: Apply behavioral science (e.g., signage with messages like “90% of people here don’t litter”) to encourage compliance, as seen in experiments by IIT Delhi.
- Address Socio-Economic Inequality:
- Reduce Scarcity Mindset: Improve access to education, jobs, and resources to lessen survival-driven rule-breaking. For instance, India’s 2020 PM Awas Yojana housing scheme reduced slum-related civic violations.
- Empower Marginalized Groups: Ensure equitable enforcement to build trust in the system, as distrust fuels non-compliance.
Challenges to Implementation
- Resistance to Change: Cultural inertia and vested interests (e.g., corrupt officials) may resist reforms.
- Resource Constraints: India’s large population and budget limitations complicate scaling infrastructure and enforcement.
- Urban-Rural Divide: Solutions must address varying literacy, income, and infrastructure levels across regions.
Conclusion
The observation that Indians follow rules better abroad than in India is grounded in real differences in enforcement, infrastructure, and social norms, though it’s not universally true. To foster law-abiding and ethico-rational behavior, India needs a multi-pronged approach: stronger enforcement, better infrastructure, civic education, cultural shifts, and socio-economic equity. Combining systemic reforms with behavioral nudges and community engagement can gradually align behavior with ethical and rational ideals, drawing on successful models like Swachh Bharat and smart city initiatives.
S855: Maritally Safer India. Visions for Homeicide Free India. HithaParivar Bharat.
Unite 4 Men’s Welfare. Or Stay away and Watch Many Mens Fare well.
Many ‘MisFamilic‘ (Anti-Family) crimes against Families by NarcWomen and NarcMen are being seen on the rise in Indian Society. SOS_India (Save Our Sons Of India).
If Your under Emotional Distress call 112 or Mens Help Line 8882498498.

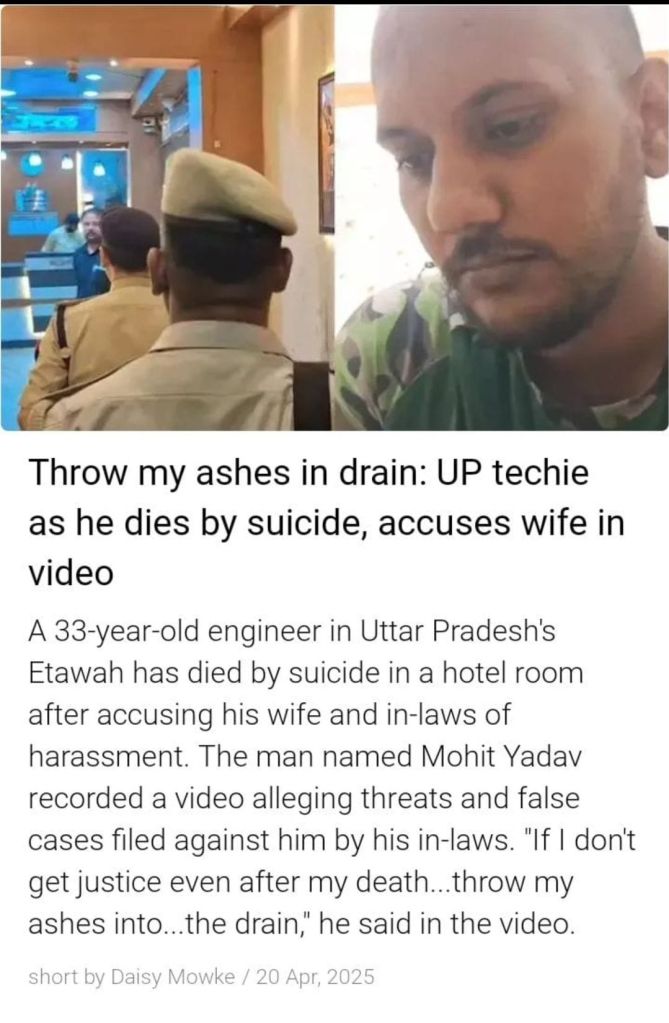
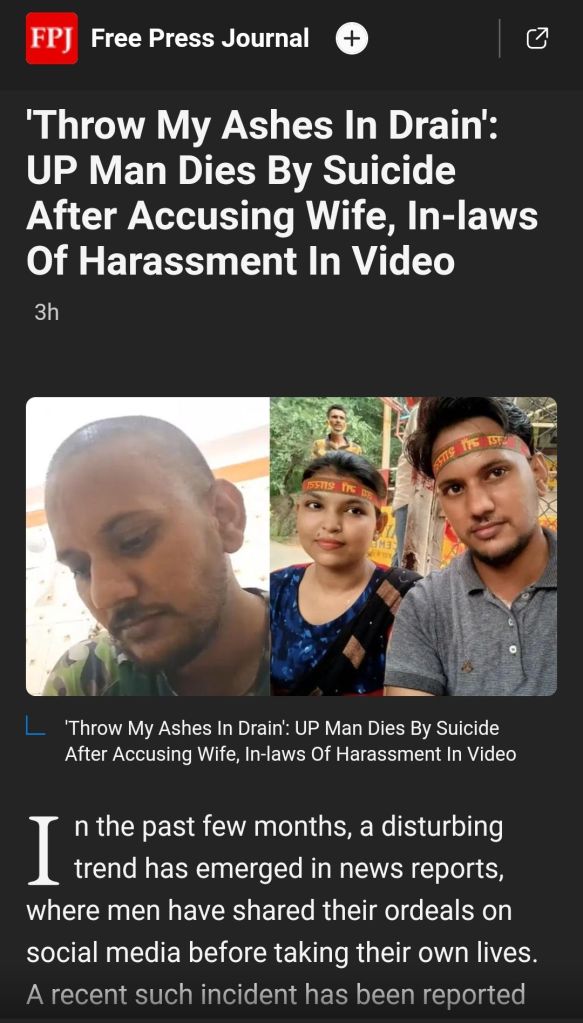
All India Mens & Family Welfare Group: https://chat.whatsapp.com/KecJokbFlP4F0azMaCyeyA

S674: How to Prevent “Suicides Contagion” in India?. Heal’Thy society
*Lets Unify Indian Brotherhoods* for Problem Solving Our Next_Gen.
Grp Mission is InterGenders Harmony & Neo Indian_SaferFamilies 4.0.