Morally, Socially, Legally & Spiritually What are the Duties, Rights & Responsibility of spouses in Indian marriages?
Simplest Equations for a Marriage & Wedding.
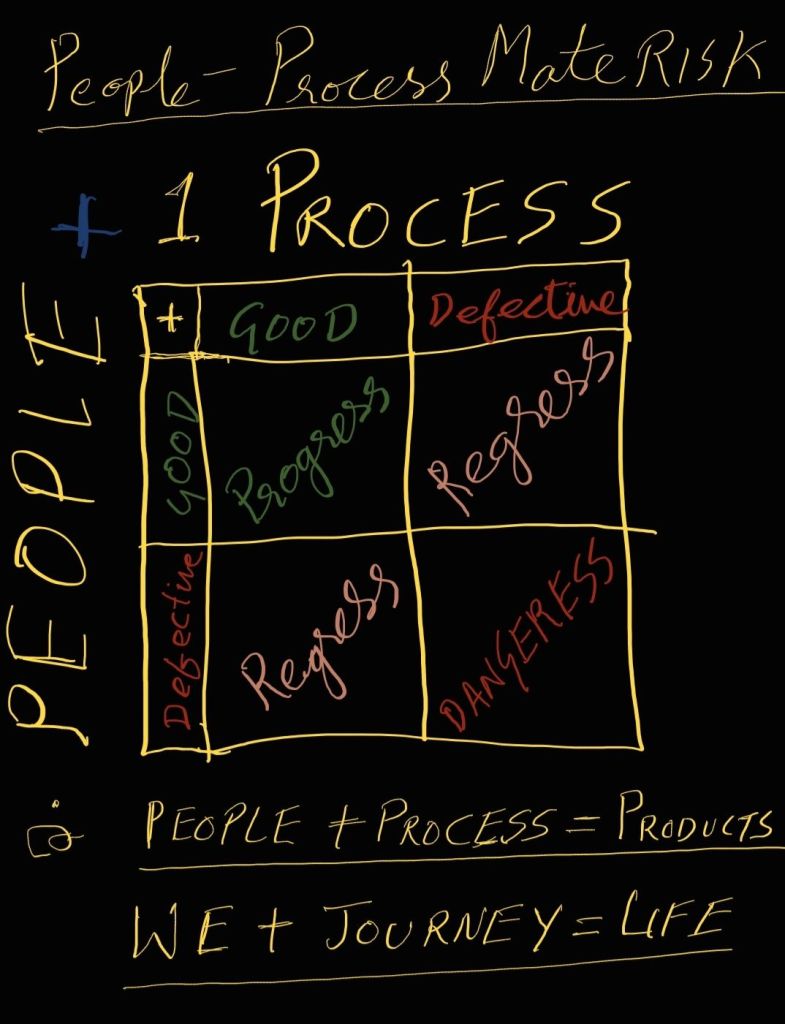
Marriage= Marriers + Maritalizers + MaritoLegal Systems.
Wedding= Marriers + Event + Officials +Witnesses
This was triggered by a question by DA in Manavamitres group for Genders Peace,
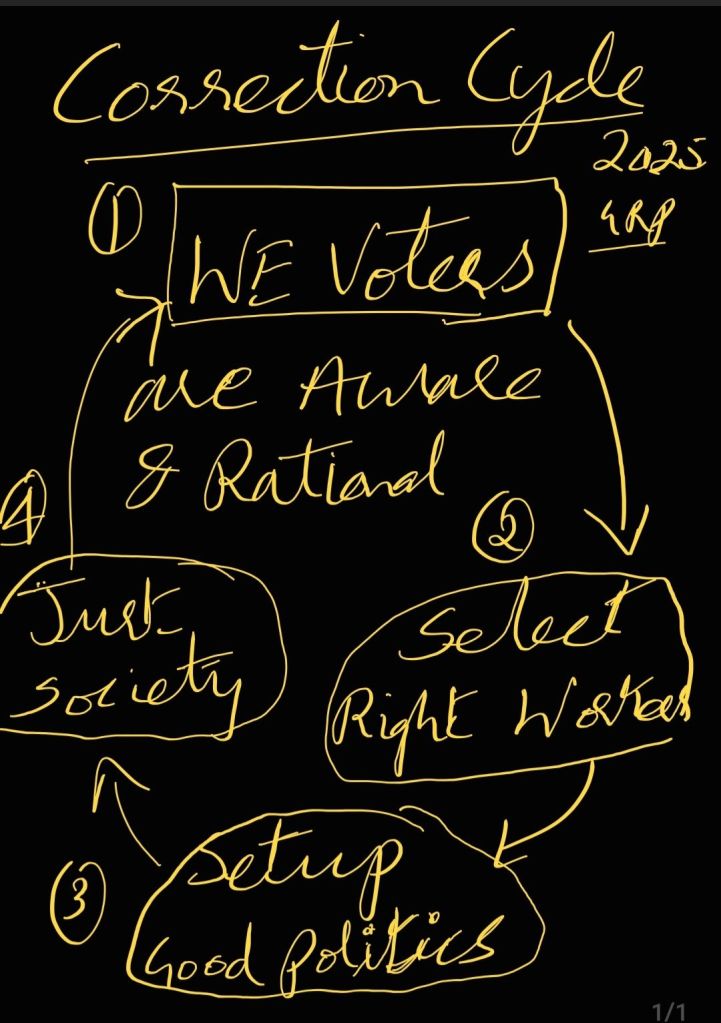
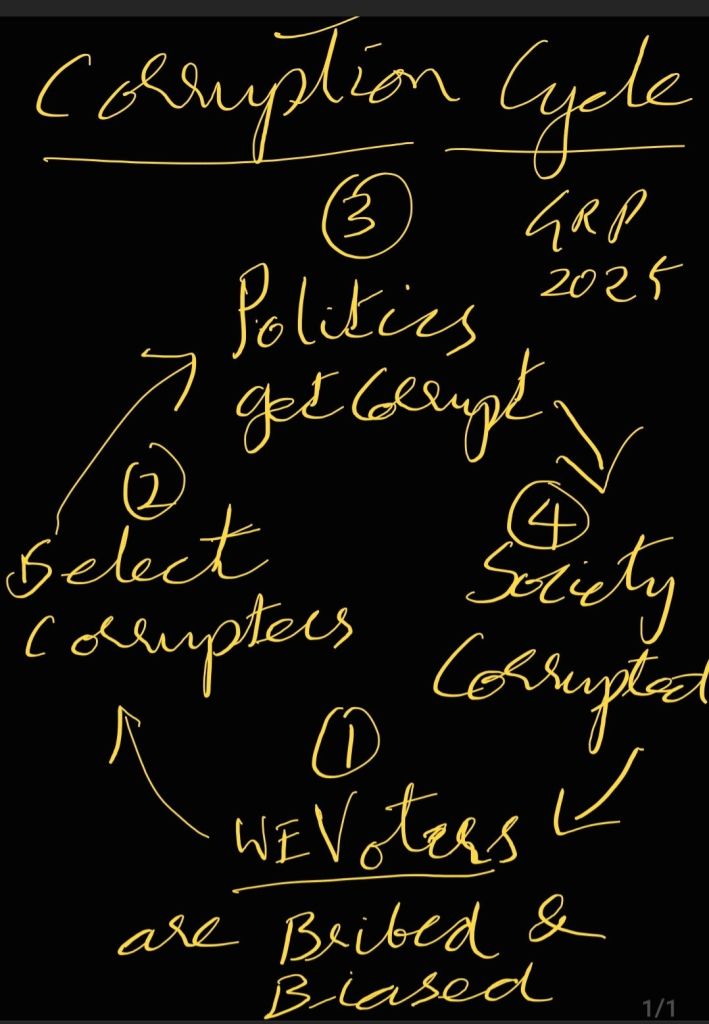
gud question.. societies, scholars & religions have attempted to define these like in customs & scriptures, constitution & legally not defined by governments, only Rights of women have been defined in Indian laws needs update with rights if husband & duties of both spouses to make pre-marital agreements easy & legally safer. instead if suffer..
In Indian weddings and marriages, the duties and rights of spouses, elders, and maritalizers are governed by a combination of moral, legal, social, and spiritual principles. Here’s a comprehensive overview:
Spouses (Marriers)
Moral and Spiritual Duties
- Mutual Respect: Treat each other with respect, dignity, and compassion.
- Loyalty and Fidelity: Remain faithful and committed to each other.
- Support and Care: Provide emotional, physical, and financial support.
- Communication: Maintain open and honest communication.
- Compromise and Understanding: Be willing to compromise and understand each other’s perspectives.
Legal Rights
- Equality: Both spouses have equal rights and responsibilities.
- Property Rights: Both spouses have equal rights to property and assets acquired during the marriage.
- Inheritance: Both spouses have equal rights to inherit each other’s property.
- Maintenance: Both spouses have the right to claim maintenance from each other.
- Divorce: Both spouses have the right to seek divorce.
Social Duties
- Family Integration: Integrate with each other’s families and respect their traditions.
- Social Responsibilities: Fulfill social responsibilities, such as participating in community events.
- Respect for Elders: Show respect and care for elders in the family.
- Host Responsibilities: Host and take care of guests, including relatives and friends.
Spiritual Duties
- Joint Spiritual Growth: Support each other’s spiritual growth and development.
- Participation in Rituals: Participate in spiritual rituals and ceremonies together.
- Respect for Each Other’s Beliefs: Respect each other’s spiritual beliefs and practices.
Elders (Maritalizers)
Moral and Spiritual Duties
- Guidance and Support: Provide guidance and support to the newlywed couple.
- Blessings and Wisdom: Offer blessings and share wisdom gained from experience.
- Respect for Traditions: Respect and pass on traditional values and customs.
- Family Unity: Promote family unity and harmony.
Legal Rights
- Decision-Making: Have a say in important family decisions, including those related to the marriage.
- Property Management: Manage and distribute family property, including ancestral assets.
- Inheritance: Have a say in the distribution of inheritance.
Social Duties
- Family Leadership: Provide leadership and guidance to the family.
- Social Responsibilities: Fulfill social responsibilities, such as participating in community events.
- Respect for Tradition: Respect and uphold family traditions and customs.
Spiritual Duties
- Spiritual Guidance: Provide spiritual guidance and support to the family.
- Ritual Participation: Participate in spiritual rituals and ceremonies.
- Passing on Spiritual Values: Pass on spiritual values and traditions to the next generation.
Maritalizers (Those Who Arrange the Marriage)
Moral and Spiritual Duties
- Fairness and Transparency: Ensure fairness and transparency in the marriage arrangement process.
- Respect for Choices: Respect the choices and decisions of the couple and their families.
- Honesty and Integrity: Maintain honesty and integrity throughout the process.
Legal Rights
- Negotiation and Agreement: Negotiate and agree on the terms of the marriage, including dowry and other financial arrangements.
- Documentation: Ensure proper documentation, including registration of the marriage.
Social Duties
- Family Representation: Represent the family in the marriage arrangement process.
- Social Etiquette: Follow social etiquette and customs during the process.
- Respect for Traditions: Respect and uphold family traditions and customs.
Spiritual Duties
- Prayers and Blessings: Offer prayers and blessings for the couple’s happiness and well-being.
- Spiritual Guidance: Provide spiritual guidance and support to the couple and their families.
Importance of Premarital Background Check
A premarital background check is essential in today’s society. It helps to:
- Verify Identity: Confirm the identity of the partner, including their name, age, and marital status.
- Check for Criminal Records: Ensure the partner does not have any criminal records or pending cases.
- Verify Education and Employment: Confirm the partner’s educational qualifications and employment status.
- Check for Financial Stability: Assess the partner’s financial stability and creditworthiness.
- Detect Potential Red Flags: Identify potential red flags, such as a history of addiction or abusive behavior.
By conducting a premarital background check, individuals can make informed decisions about their partner and ensure a safer and more secure marriage.
In summary, the duties and rights of spouses, elders, and maritalizers in Indian weddings and marriages are guided by a combination of moral, legal, social, and spiritual principles. These principles
Here are some citations and references from Indian laws that support the duties and rights mentioned earlier:
Spouses (Marriers)
Moral and Spiritual Duties
- Section 13 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: States that a marriage can be dissolved if the spouse has been guilty of cruelty, desertion, or adultery. (1)
- Section 18 of the Hindu Adoptions and Maintenance Act, 1956: Provides for the maintenance of a wife by her husband. (2)
Legal Rights
- Section 14 of the Hindu Succession Act, 1956: States that a wife has equal rights to property and assets acquired during the marriage. (3)
- Section 125 of the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973: Provides for the maintenance of a wife by her husband. (4)
- The Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005: Protects women from domestic violence and provides for their rights and entitlements. (5)
Social Duties
- Section 3 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: States that a marriage is void if it is not performed in accordance with the customs and rituals of the parties. (1)
- Section 11 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: Provides for the registration of marriages. (1)
Spiritual Duties
- Section 7 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: States that a marriage is valid if it is performed in accordance with the customs and rituals of the parties. (1)
Elders (Maritalizers)
Moral and Spiritual Duties
- Section 3 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: States that a marriage is void if it is not performed in accordance with the customs and rituals of the parties. (1)
- Section 10 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: Provides for the duties of the guardian in respect of the minor. (1)
Legal Rights
- Section 6 of the Hindu Succession Act, 1956: States that a father has the right to dispose of his property by will or gift. (3)
- Section 8 of the Hindu Succession Act, 1956: Provides for the devolution of property on the death of a Hindu. (3)
Social Duties
- Section 3 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: States that a marriage is void if it is not performed in accordance with the customs and rituals of the parties. (1)
- Section 11 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: Provides for the registration of marriages. (1)
Spiritual Duties
- Section 7 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: States that a marriage is valid if it is performed in accordance with the customs and rituals of the parties. (1)
Maritalizers (Those Who Arrange the Marriage)
Moral and Spiritual Duties
- Section 3 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: States that a marriage is void if it is not performed in accordance with the customs and rituals of the parties. (1)
- Section 10 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: Provides for the duties of the guardian in respect of the minor. (1)
Legal Rights
- Section 6 of the Hindu Succession Act, 1956: States that a father has the right to dispose of his property by will or gift. (3)
- Section 8 of the Hindu Succession Act, 1956: Provides for the devolution of property on the death of a Hindu. (3)
Social Duties
- Section 3 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: States that a marriage is void if it is not performed in accordance with the customs and rituals of the parties. (1)
- Section 11 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: Provides for the registration of marriages. (1)
Spiritual Duties
- Section 7 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: States that a marriage is valid if it is performed in accordance with the customs and rituals of the parties. (1)
Importance of Premarital Background Check
- Section 12 of the Special Marriage Act, 1954: Provides for the verification of the identity and age of the parties. (6)
- Section 13 of the Special Marriage Act, 1954: States that a marriage can be declared null and void if it is not valid according to the law. (6)
References:
- The Hindu Marriage Act, 1955 (Act 25 of 1955).
- The Hindu Adoptions and Maintenance Act, 1956 (Act 78 of 1956).
- The Hindu Succession Act, 1956 (Act 30 of 1956).
- The Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 (Act
Here are the analyses, validations, modifications, and refinements of the given statements with citations:
Wedding Equation
Original Statement
Wedding = Marriers + Event + Officials + Witnesses
Analysis
Marriers: Refers to the couple getting married. (Section 3 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955) (1)
Event: Refers to the wedding ceremony. (Section 7 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955) (1)
Officials: Refers to the persons authorized to perform the wedding ceremony, such as priests or registrars. (Section 7 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955) (1)
Witnesses: Refers to the persons who attend the wedding ceremony and witness the marriage. (Section 11 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955) (1)
Validation
The equation is mostly accurate, but it can be refined to include other essential elements.
Modified Equation
Wedding = Marriers + Event + Officials + Witnesses + Marriage Registration
Citation
Section 11 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: Provides for the registration of marriages. (1)
Marriage Equation
Original Statement
Marriage = Marriers + Maritalizers + MaritoLegal Systems
Analysis
Marriers: Refers to the couple getting married. (Section 3 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955) (1)
Maritalizers: Refers to the persons who arrange the marriage, such as parents or guardians. (Section 10 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955) (1)
MaritoLegal Systems: Refers to the legal systems governing marriage, such as the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955. (1)
Validation
The equation is mostly accurate, but it can be refined to include other essential elements.
Modified Equation
Marriage = Marriers + Maritalizers + MaritoLegal Systems + Social and Cultural Norms
Citation
Section 3 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: States that a marriage is void if it is not performed in accordance with the customs and rituals of the parties. (1)
Section 7 of the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955: States that a marriage is valid if it is performed in accordance with the customs and rituals of the parties. (1)
References:
The Hindu Marriage Act, 1955 (Act 25 of 1955).
The Hindu Adoptions and Maintenance Act, 1956 (Act 78 of 1956).
The Hindu Succession Act, 1956 (Act 30 of 1956).
The Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 (Act 2 of 1974).
The Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005 (Act 43 of 2005).
The Indian Divorce Act, 1869 (Act 4 of 1869).
The Dissolution of Muslim Marriages Act, 1939 (Act 8 of 1939).
The Muslim Women (Protection of Rights on Divorce) Act, 1986 (Act 25 of 1986).
The Indian Christian Marriage Act, 1872 (Act 15 of 1872).