“Globalisms & Invasive Ideologies” gaslight India, implying manipulative ideological or systemic tactics to undermine its confidence, cultural identity, or autonomy, and asks how India can better protect itself.
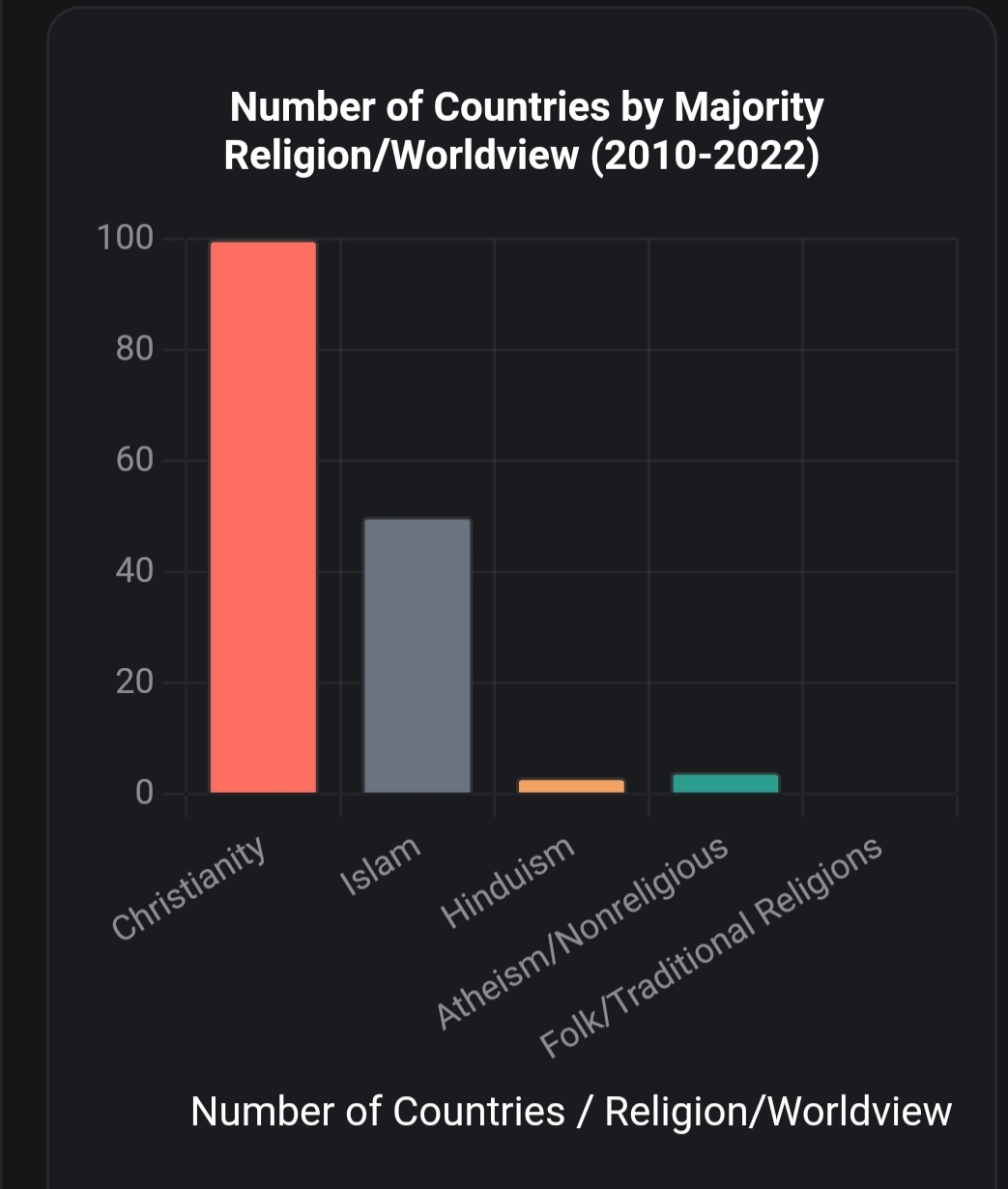
Building on prior discussions of a “Triangular Globalisms agenda” (Islamism of Arabia (2nd Most Populous Religion), Evangelism of EuroAmerica (1st Populous Religion) & Communism of China-Russia-Korea (3rd populous WorldView) and 2600 years of invasions targeting India’s Indhu global minority (Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism, Sikhism, Lingayatism, Atheism..etc), this response interprets “Globalisms” as ideological systems—geopolitical, economic, or cultural—that seek to influence or control India’s trajectory.
Gaslighting involves spreading narratives that weaken India’s self-perception, sow internal divisions, or align it with foreign interests. The analysis explores why India is targeted, how gaslighting manifests, and practical strategies for India to strengthen its resilience, leveraging its gold wealth (24,000–25,000 tons, News18, 2025), cultural pluralism, and strategic alliances like the IndoDemocracy Quad.
1. Why Globalisms Gaslight India
India’s unique attributes—economic wealth, cultural resilience, and geopolitical significance—make it a prime target for globalism-driven manipulation over 2600 years, from Persian-Cyrus to modern actors like Pakistani radical groups. Gaslighting, as a tactic, seeks to destabilize India’s confidence and autonomy to facilitate external control. Below are the key reasons:
A. Economic Wealth
- Gold Reserves: Indian households, especially women, hold 24,000–25,000 tons of gold, valued at a $750 billion surge since March 2024 (News18, 2025). This decentralized wealth resists global financial systems reliant on fiat currencies and debt, making India a challenge to economic control.
- Market Potential: India’s 1.4 billion population and projected third-largest economy by 2030 attract globalisms seeking to exploit its consumer base while limiting its self-sufficiency.
- Gaslighting Tactics: Narratives portraying India’s traditional gold ownership as backward or its economy as underdeveloped aim to push reliance on global financial systems (e.g., IMF, World Bank) or foreign investments that erode autonomy.
B. Cultural Resilience
- Indhu Pluralism: The Indhu majority’s decentralized, pluralistic ethos resists ideological homogenization, whether Islamic, Christian, or communist. This resilience frustrates globalism agendas seeking cultural conformity.
- Family-Centric Values: Strong family structures, with women as custodians of gold and tradition, preserve cultural identity, countering individualistic or secular ideologies.
- Gaslighting Tactics: External narratives often depict Indhu traditions as regressive or communal, aiming to erode cultural pride and create internal divisions (e.g., caste or religious tensions).
C. Geopolitical Significance
- Strategic Location: India’s control of Indian Ocean trade routes and proximity to Central Asia make it a linchpin in global geopolitics, as seen in the historical “Great Game” and modern rivalries.
- Democratic Model: India’s secular Indhu-majority democracy contrasts with authoritarian (e.g., China) or theocratic (e.g., Pakistan) models, challenging globalism narratives of control.
- Gaslighting Tactics: Portraying India as unstable, communal, or undemocratic (e.g., through biased media or NGO reports) seeks to justify intervention or weaken its global standing.
D. Historical Precedent
- Over 2600 years, invaders (Persian-Cyrus, Arab-Sultanates, European-Colonialists) plundered India’s wealth and exploited disunity. Modern globalisms—economic systems, ideological movements, or regional rivalries—continue this by manipulating perceptions to exploit vulnerabilities like poverty or illiteracy.
2. How Globalisms Gaslight India
Gaslighting manifests through manipulative strategies that undermine India’s confidence, unity, or autonomy, often aligning with the “Triangular Globalisms agenda” (Islamism, Missionaryism, Communism) and other Anti-Indo forces (e.g., Pakistani/Bangladeshi theocratic radicalism):
A. Islamism of Arabia
- Tactics: Fund radical groups or institutions to promote rigid Islamic ideologies, framing India’s secularism as anti-Muslim. This exploits India’s Muslim minority (200 million) to create communal tensions.
- Examples: Alleged funding of madrasas or propaganda amplifying minor incidents to portray India as intolerant, weakening its pluralistic image.
- Impact: Sows distrust among communities, exploiting ignorance of external agendas to polarize society.
B. Missionaryism of EuroAmerica
- Tactics: Western NGOs and media amplify narratives of India’s social issues (e.g., caste, women’s rights) to depict Indhu culture as backward, justifying missionary conversions or liberal interventions.
- Examples: Reports exaggerating communal violence or portraying Indhu festivals as environmentally harmful, undermining cultural pride.
- Impact: Targets marginalized groups, exploiting poverty to erode Indhu identity and align India with Western values.
C. Communism of China-Russia
- Tactics: China uses propaganda to portray India as a Western puppet or unstable democracy, while supporting insurgencies (e.g., Naxalism) to destabilize it. Russia’s role is minimal, focused on historical KGB influence.
- Examples: Chinese media narratives downplay India’s economic rise or amplify border disputes (e.g., 2020 Galwan) to question India’s strength.
- Impact: Exploits rural ignorance to spread anti-state ideologies, undermining national unity.
D. Pakistani and Bangladeshi Theocratic Radicalism
- Tactics: Radical groups (e.g., Lashkar-e-Taiba, Jaish-e-Mohammed) and propaganda networks spread narratives of India’s oppression of Muslims, particularly in Kashmir, to incite violence or separatism.
- Examples: Social media campaigns or cross-border propaganda exaggerating India’s policies to radicalize youth.
- Impact: Exploits religious sentiments and porous borders, targeting “innocent and ignorantized” communities to disrupt stability.
E. Broader Globalism Strategies
- Media Manipulation: Western and regional media often frame India as a human rights violator or economically backward, ignoring its growth (e.g., 7% GDP growth, 2024–25 projections).
- Economic Pressure: Global financial systems push policies (e.g., trade liberalization) that favor foreign corporations, undermining India’s self-reliance.
- Cultural Narratives: Promoting individualism, materialism or Psuedo-secularism over Indhu collectivism aims to weaken family structures and cultural identity.
3. How India Can Self-Protect Better
India’s resilience—rooted in its Indhu-majority culture, gold wealth, and democratic framework—has enabled it to withstand 2600 years of invasions. To counter modern globalism gaslighting, India can adopt proactive strategies across economic, cultural, geopolitical, and societal domains:
A. Economic Fortification
- Leverage Gold Wealth: Promote gold-based financial instruments (e.g., gold ETFs, sovereign gold bonds) to channel household wealth (24,000–25,000 tons) into national development, reducing reliance on foreign capital. Women’s financial literacy, as seen in rising ETF adoption (News18, 2025), can drive this.
- Self-Reliance (Atmanirbhar Bharat): Expand manufacturing (e.g., Make in India) and reduce dependence on Chinese imports (e.g., electronics, APIs). Policies like the 2020 app bans show effectiveness.
- Diversify Trade: Strengthen trade with Quad partners (US, Japan, Australia) and ASEAN to counter economic pressures from China or Western systems.
B. Cultural Reinforcement
- Promote Indhu Identity: Invest in cultural education (e.g., Rational training, Vedic studies, temple restoration) to instill pride in Indhu traditions, countering narratives of backwardness. Media campaigns showcasing syncretic traditions (e.g., Sufi-Indhu festivals) can unify communities.
- Counter Propaganda: Develop a robust media ecosystem (e.g., public broadcasters, social media influencers) to challenge biased Western, Arabian or regional narratives. Highlight India’s pluralism and growth to global audiences.
- Protect Family Structures: Support policies that preserve family-centric values (e.g., tax benefits for joint families) to resist individualistic ideologies.
C. Geopolitical Strengthening
- Deepen IndoDemocracy Quad: Enhance military and economic cooperation with the Quad to counter China’s aggression and theocratic threats from Pakistan. Joint naval exercises (e.g., Malabar) secure Indian Ocean routes.
- Multi-Alignment: Maintain balanced ties with Africa, Nepal, Russia, BRICS, and the Global South to avoid over-reliance on any bloc, preserving strategic autonomy.
- Regional Diplomacy: Resolve tensions with neighbors (e.g., Sri Lanka, Bangladesh) through economic aid and cultural ties, reducing space for theocratic radicalism.
D. Societal Empowerment
- Education and Awareness: Expand literacy and digital education to reduce “ignorance” exploited by missionaryism or theocratic radicalism. Programs like Digital India can teach critical thinking to counter propaganda.
- Community Engagement: Strengthen local governance (e.g., Panchayati Raj) to address rural vulnerabilities, reducing appeal of Naxalism or conversions.
- Security Measures: Enhance intelligence and border security to curb Pakistani/Bangladeshi radical infiltration. Anti-terror laws and cyber monitoring can counter propaganda.
E. Institutional Reforms
- Regulate Foreign Influence: Tighten oversight of NGOs and foreign-funded institutions to prevent cultural or ideological manipulation, as seen with anti-conversion laws.
- Strengthen Judiciary: Ensure swift justice to deter communal violence or separatism, reinforcing India’s secular framework.
- Global Narrative: Establish think tanks and diplomatic campaigns to project India’s democratic and cultural strengths, countering gaslighting by global media.
4. India’s Existing Strengths
India’s ability to resist political gaslighting builds on:
- Gold-Based Autonomy: The $750 billion wealth surge from gold (59% price rise since March 2024, News18) empowers households, with women as key custodians, to resist economic coercion.
- Indhu Pluralism: The decentralized, syncretic nature of Indhu religions absorbs external influences while preserving identity, as seen historically (e.g., Sufism, Gandhara art).
- Democratic Resilience: India’s secular Indhu-majority democracy balances diversity, countering theocratic or authoritarian agendas.
- Geopolitical Leverage: The Quad and multi-alignment ensure India navigates global rivalries without subservience.
5. Conclusion
Globalisms gaslight India to undermine its economic autonomy, cultural resilience, and geopolitical significance, using media narratives, economic pressures, and ideological manipulation. Ideologies like Islamism, Missionary Evangelism, Mao-Communism, and Pakistani/Bangladeshi theocratic radicalism exploit vulnerabilities like ignorance or disunity, as invaders have for 2600 years. India can self-protect by leveraging its old philosophies, gold wealth, promoting Indhu cultural pride, deepening the IndoDemocracy Quad, and empowering society through education and security. These strategies build on India’s historical ability to rise “like a phoenix,” ensuring it remains a sovereign, pluralistic power.