Human Theory of Social Relativity.
Understanding LIFE = Lived Individuals Formed Experiences..
What we see is just visible 10 % what underlies that is the unseen 90%.
This post started by a Question 2 famous people with similar sounding names (Kalam & Kasab) one Became the missile man scientist honored with state burial, & another became the mission man a terrorist hanged by state judicial. What Differentiated their Lives and one Rational member told its due to the environment, then we inquired what was the cause for Environment we arrived at Its the Education system & Experiences.. further on..
Thiz post tries to see deeper at the ICEBerg model of Life.
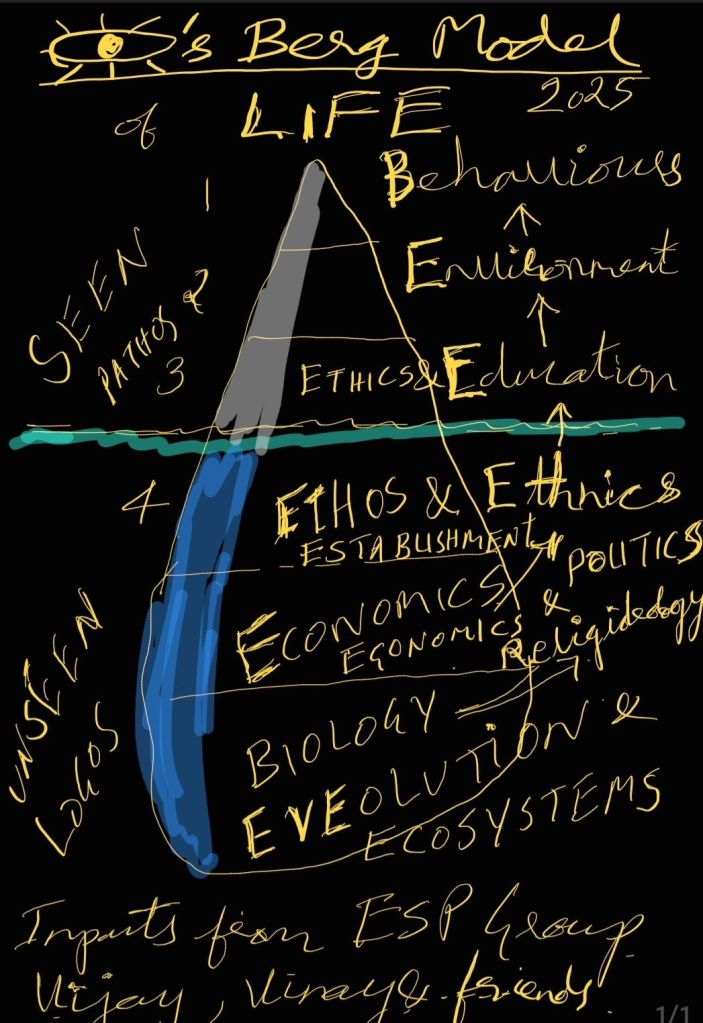
Here’s a simplified version of the previous model, condensed into an Iceberg Model with three sections:
Iceberg Model
Visible 10%: Behavior and Outcomes
- Life outcomes (health, happiness, success)
- Behavior (choices, actions, decisions)
- People (individuals, communities, societies)
Invisible 40%: Environmental and Socio-Cultural Influences
- Environment (physical, social, economic)
- Education and experience
- Ethos, culture, and ethnicity
- Socioeconomic factors (poverty, inequality)
- Religion, ideology, and politics
Invisible 50%: Underlying Processes, Principles, and Purposes
- Biological and evolutionary factors
- Evolutionary processes (genetic variation, natural selection)
- Fundamental human needs and drives (survival, belonging, meaning)
- Universal principles and values (compassion, fairness, justice)
- Ultimate purposes and goals (self-actualization, transcendence)
This Iceberg Model illustrates how the visible behaviors and outcomes of individuals and societies are influenced by a larger set of invisible factors, including environmental and socio-cultural influences, as well as underlying processes, principles, and purposes.
What is progression with citation for below Ideas.. ” Life depends on Behaviour, which depends on Environment which depends on Education or Experience which depends on Ethos, Culture or Ethnicity, which depends on Socio economics & politics which depends on evolution. and more..” explain with sources..
The concept you’re describing is a hierarchical, interconnected model of factors influencing human behavior and life outcomes. Here’s a breakdown of the progression with citations:
1. Life depends on Behaviour
- Research suggests that behavior plays a crucial role in determining life outcomes, including physical and mental health (World Health Organization, 2019) [1].
- Behavioral choices, such as diet and exercise, can significantly impact life expectancy and quality of life (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020) [2].
2. Behaviour depends on Environment
- The environment has a profound impact on behavior, with factors such as urbanization, pollution, and climate change influencing human behavior and well-being (United Nations, 2020) [3].
- Environmental factors, such as access to green spaces and socioeconomic conditions, can shape behavioral choices and life outcomes (World Health Organization, 2018) [4].
3. Environment depends on Education or Experience
- Education and experience can shape an individual’s perception of their environment and influence their behavioral choices (Bandura, 1977) [5].
- Formal education and informal experiences can provide individuals with the knowledge, skills, and values necessary to navigate their environment effectively (UNESCO, 2019) [6].
4. Education or Experience depends on Ethos, Culture or Ethnicity
- Cultural and ethnic background can significantly influence an individual’s values, beliefs, and behaviors, shaping their educational and experiential opportunities (Hall, 1959) [7].
- Ethos and cultural norms can impact access to education and experiences, perpetuating social inequalities (Bourdieu, 1977) [8].
5. Ethos, Culture or Ethnicity depends on Socio economics
- Socioeconomic factors, such as poverty and inequality, can shape cultural values and norms, influencing educational and experiential opportunities (Sen, 1999) [9].
- Socioeconomic conditions can impact access to resources, such as education and healthcare, which in turn shape cultural and ethnic identities (Giddens, 1998) [10].
6. Socio economics depends on Religion, ideology & politics
- Religious beliefs and ideologies can shape socioeconomic policies and systems, influencing access to resources and opportunities (Weber, 1905) [11].
- Political systems and ideologies can impact socioeconomic conditions, such as poverty and inequality, which in turn shape cultural and ethnic identities (Marx, 1867) [12].
7. Religion, ideology & politics depends on Biology & evolution
- Evolutionary processes have shaped human biology and behavior, influencing the development of religious beliefs and ideologies (Richerson & Boyd, 2005) [13].
- Biological and evolutionary factors, such as genetic variation and natural selection, have influenced human social and cultural development, including the emergence of complex societies and political systems (Diamond, 1997) [14].
This hierarchical model highlights the complex interplay between factors influencing human behavior and life outcomes. While this model is not exhaustive, it illustrates the importance of considering the broader social, cultural, and environmental contexts in which human behavior is shaped.
References:
[1] World Health Organization. (2019). World Health Statistics 2019.
[2] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020). Healthy People 2030.
[3] United Nations. (2020). Sustainable Development Goals.
[4] World Health Organization. (2018). Environmental Health.
[5] Bandura, A. (1977). Social Learning Theory.
[6] UNESCO. (2019). Education for Sustainable Development.
[7] Hall, E. T. (1959). The Silent Language.
[8] Bourdieu, P. (1977). Outline of a Theory of Practice.
[9] Sen, A. (1999). Development as Freedom.
[10] Giddens, A. (1998). The Third Way.
[11] Weber, M. (1905). The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism.
[12] Marx, K. (1867). Das Kapital.
[13] Richerson, P. J., & Boyd, R. (2005). Not by Genes Alone.
[14] Diamond, J. (1997). Guns, Germs, and Steel.
Growing in multiple aspects of life requires intentional effort, dedication, and a willingness to learn and adapt. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you grow in various areas:
Spiritual Growth
- Meditation and mindfulness: Practice mindfulness meditation, yoga, or tai chi to connect with your inner self.
- Read spiritual texts: Explore sacred texts, such as the Bible, Quran, or Bhagavad Gita, to deepen your understanding of spirituality.
- Connect with nature: Spend time in nature, appreciate its beauty, and recognize the interconnectedness of all living beings.
- Practice gratitude: Reflect on the things you’re thankful for each day to cultivate a sense of gratitude and positivity.
Familial Growth
- Communicate effectively: Practice active listening, express yourself clearly, and resolve conflicts in a constructive manner.
- Spend quality time: Regularly schedule quality time with family members, engaging in activities that promote bonding and shared experiences.
- Show appreciation: Express gratitude and appreciation for your family members, celebrating their achievements and supporting them through challenges.
- Create traditions: Establish and maintain family traditions, such as weekly dinners or annual vacations, to foster a sense of connection and belonging.
Relational Growth
- Nurture empathy: Practice putting yourself in others’ shoes, actively listening to their perspectives, and showing understanding and compassion.
- Develop healthy boundaries: Establish and maintain clear boundaries in your relationships, prioritizing your own needs and well-being.
- Cultivate emotional intelligence: Recognize, understand, and manage your emotions to improve your relationships and communication skills.
- Invest in meaningful relationships: Prioritize relationships that bring value, support, and joy to your life, and invest time and effort in nurturing them.
Intellectual Growth
- Read widely: Engage in regular reading, exploring various subjects, genres, and authors to broaden your knowledge and perspectives.
- Take online courses: Utilize online platforms, such as Coursera, Udemy, or edX, to learn new skills, expand your knowledge, and stay up-to-date with industry trends.
- Attend workshops and seminars: Participate in workshops, conferences, and seminars to learn from experts, network with peers, and stay informed about the latest developments in your field.
- Practice critical thinking: Engage in critical thinking exercises, such as solving puzzles, brain teasers, or debating topics, to improve your analytical skills and problem-solving abilities.
Professional Growth
- Set clear goals: Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for your career, breaking them down into smaller, manageable objectives.
- Develop new skills: Identify areas for improvement and invest in training, courses, or mentorship to enhance your skills and stay competitive in your industry.
- Network strategically: Attend industry events, join professional organizations, and connect with peers and thought leaders to expand your network and stay informed about industry trends.
- Seek feedback and learn from criticism: Request constructive feedback from colleagues, managers, or mentors, and use it as an opportunity to learn, grow, and improve.
Social Growth
- Join social clubs or groups: Engage in hobbies or interests with like-minded individuals, joining clubs, groups, or organizations that align with your passions.
- Volunteer: Participate in volunteer work, donating your time and skills to causes that resonate with you, and expanding your social circle while making a positive impact.
- Attend community events: Participate in local events, such as festivals, concerts, or street fairs, to connect with your community and meet new people.
- Practice active listening: Engage in meaningful conversations, actively listening to others, and showing genuine interest in their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
Physical Growth
- Establish a workout routine: Engage in regular physical activity, such as cardio, strength training, or flexibility exercises, to improve your overall health and well-being.
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on consuming a variety of whole, nutrient-dense foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Get enough sleep: Prioritize sleep, aiming for 7-9 hours of restful sleep each night, to help your body recover, repair, and recharge.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day, aiming for at least 8 cups (64 ounces) daily, to help your body function optimally.
Financial Growth
- Create a budget: Establish a comprehensive budget, tracking your income and expenses, to gain clarity on your financial situation and make informed decisions.
- Invest wisely: Explore investment options, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, to grow your wealth over time, and consider consulting with a financial advisor.
- Build an emergency fund: Save 3-6 months’ worth